Ethernet technology undoubtedly plays a key role in modern networks. This article will explore the technical limitations of Ethernet transmission distance. We will first review the transmission distance provisions in Ethernet technical standards and analyze the key factors that affect Ethernet transmission distance. Next, we will describe the over-distance transmission problems encountered in actual application scenarios and analyze the technical bottlenecks that cause Ethernet over-distance.
Subsequently, we will introduce the method of using repeaters, hubs and other equipment to extend the distance, and discuss the technology of integrating optical fiber and Ethernet to extend the transmission range. In addition, we will explain how PoE technology adds energy to Ethernet transmission and illustrate the advantages of PoE in extended-distance applications.

Standard requirements for Ethernet transmission distance
Let me review the transmission distance provisions in the Ethernet technical standards for you, and analyze the key factors that affect the Ethernet transmission distance.
Provisions on transmission distance in Ethernet technical standards:
Classic Ethernet (10Base-T) standard:
- The maximum transmission distance is 100 meters.
- Use twisted pair (Category 3 or better) as the transmission medium.
Fast Ethernet (100Base-TX) standard:
- The maximum transmission distance is also stipulated as 100 meters.
- Requires the use of higher specification Category 5 or 5e twisted pair.
Gigabit Ethernet (1000Base-T) standard:
- The maximum transmission distance is still 100 meters.
- Category 5e or 6 twisted pair must be used.
Key factors affecting Ethernet transmission distance:
Transmission medium:
- The type of network cable and shielding performance directly determine the transmission distance.
- Using higher specification network cables can extend the transmission distance.
Signal attenuation:
- As the transmission distance increases, the signal will be severely attenuated.
- Excessive transmission distance will cause signal distortion and prevent normal reception.
Interference noise:
- External electromagnetic interference can cause interference and noise to Ethernet signals.
- This will also limit the effective distance of Ethernet transmission.
Relay equipment:
- By adding relay equipment such as repeaters and switches, the transmission distance can be extended.
- But too many relays will increase delay and power consumption and reduce network performance.
In summary, Ethernet technical standards have clear regulations on transmission distance, which is mainly limited by factors such as transmission medium performance, signal attenuation, and interference noise. In practical applications, it is necessary to select the appropriate network cable type and relay equipment according to the specific situation to meet the required transmission distance requirements.
Realistic challenges of Ethernet transmission distance
Let me describe to you the Ethernet over-distance transmission problem encountered in actual application scenarios, and analyze the technical bottlenecks that cause this problem.
Ethernet over-distance transmission problems encountered in actual application scenarios:
Large campus/enterprise network:
- Network coverage in campuses or large enterprises often exceeds the standard distance of 100 meters.
- A large number of relay devices need to be deployed to extend the transmission range, which increases the complexity of deployment.
Monitoring/Building Automation Applications:
- Surveillance cameras and building automation equipment are often located far away from the computer room.
- The standard distance of 100 meters cannot cover all device locations that need to be connected.
Industrial control network:
- Equipment on a factory floor or in a warehouse environment may be dispersed.
- Standard Ethernet transmission distance cannot meet the needs of such application scenarios.
Technical bottlenecks causing Ethernet over-distance:
Signal attenuation problem:
- As the transmission distance increases, the signal in the cable will suffer severe attenuation.
- Excessive attenuation will cause signal distortion and cannot be correctly interpreted by the receiving device.
Electromagnetic interference problem:
- There are numerous sources of electromagnetic interference in industrial or built environments.
- Long-distance transmission is more susceptible to interference, causing data transmission errors.
Relay equipment power consumption problem:
- Relay equipment deployed to extend transmission distance will increase overall power consumption.
- Especially in scenes far away from power sources, power supply becomes a big challenge.
Network delay problem:
- Excessive relay devices will increase end-to-end network latency.
- This may affect time-sensitive applications such as industrial control.
In general, there are a large number of requirements beyond the standard Ethernet transmission distance in actual application scenarios, which brings many challenges to network deployment. Solving technical problems such as signal attenuation, interference noise, and power consumption limitations is the key to breaking through the bottleneck of Ethernet over-distance transmission.
Measures to increase Ethernet transmission distance
Let me introduce to you several main measures to increase the transmission distance of Ethernet:
Use repeaters, hubs and other equipment to extend the distance:
Repeater:
- Repeaters amplify and regenerate Ethernet signals, thereby extending transmission distance.
- Standard Ethernet repeaters can extend the transmission range to about 2.5 kilometers.
Hub:
- A hub combines multiple Ethernet lines into a larger network.
- Through multi-level hub deployment, the transmission range can be further expanded.
Note:
- Too many relay devices will increase delay and power consumption and reduce network performance.
- The deployment location and quantity of relay equipment need to be reasonably planned based on actual needs.
Integration of optical fiber and Ethernet to expand transmission range:
Fiber optic Ethernet:
- Using optical fiber as the transmission medium can greatly increase the transmission distance of Ethernet.
- The maximum transmission distance of optical fiber Ethernet can reach tens of kilometers, far exceeding that of twisted pair.
Fiber to Ethernet converter:
- The interconnection between optical fiber and Ethernet can be achieved through fiber optic to Ethernet converters.
- Integrate fiber optic cabling with Ethernet equipment to expand network coverage.
Application scenarios:
- Applicable to scenarios such as large campus networks, factory automation, and monitoring systems.
- Can make full use of the long-distance transmission advantages of optical fiber to solve the limitations of Ethernet transmission.
In short, the use of relay equipment such as repeaters and hubs, as well as fiber-to-Ethernet conversion solutions, are common and effective measures to increase the transmission distance of Ethernet. In practical applications, the optimal solution should be selected based on specific needs and a balance should be found between expanding coverage and maintaining network performance.
Extended Ethernet transmission distance based on PoE technology
Let me explain to you how PoE (Power over Ethernet) technology can extend the transmission distance of Ethernet and its technical advantages in this regard.
How PoE technology adds energy to Ethernet transmission:
PoE power supply mechanism:
- PoE technology can provide power supply to terminal equipment through Ethernet cables.
- This integrated power supply function can make up for the lack of the device’s own power supply.
PoE power supply energy:
- The PoE standard stipulates that it can provide up to 100W power supply.
- This extra power can be used to push Ethernet signals farther over the cable.
Power supply control mechanism:
- PoE switches can automatically detect and identify power supply needs and provide appropriate power.
- Intelligent power supply control helps improve transmission distance and energy efficiency.
Technical advantages of PoE in extended distance applications:
Simplify deployment:
- PoE terminal equipment does not require a separate power cord and only uses an Ethernet cable.
- This greatly reduces the complexity and cost of network deployment.
Enhanced flexibility:
- PoE power supply can deploy equipment in environments without power sockets.
- Improves the flexibility of device deployment and is suitable for complex application scenarios.
Reliability improvement:
- PoE power supply ensures the stable operation of terminal equipment and avoids service interruption due to power outages.
- Conducive to improving system reliability in key application scenarios.
Power supply expansion capability:
- By cascading relay devices, PoE can provide power over longer distances.
- This makes the expansion of Ethernet transmission distance more feasible and economical.
In short, PoE technology provides an effective solution for extending Ethernet transmission distance by integrating the power supply function on Ethernet cables, and has many advantages such as simplified deployment and improved reliability. This makes it popular in applications such as surveillance and building automation.
Summary
Solving the technical limitations of Ethernet transmission distance is crucial to building an efficient and stable network. Our company has long been focused on the R&D and production of network communication equipment and its supporting products, and has rich industry experience. Our Ethernet transmission equipment, such as repeaters, PoE switches, etc., have reached industry-leading levels in key indicators such as transmission distance and power consumption, and can effectively overcome the technical bottleneck of Ethernet over-distance.
Whether you need to deploy a wide-coverage monitoring system or an industrial automation network, we can provide you with customized solutions. At the same time, our technical team will provide you with all-round support, including on-site survey, solution design, and equipment debugging and other services. Contact us today to learn more details about Ethernet transmission distance extension.
Ethernet transmission distance restrictions FAQ
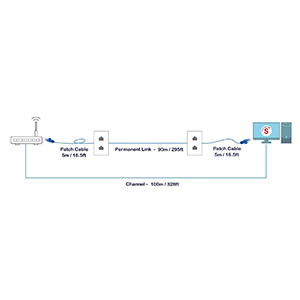
The standard maximum distance for Ethernet transmission over twisted-pair copper cables (such as Cat5e or Cat6) is 100 meters (328 feet).
Key factors include the cable type, cable quality, data rate, electromagnetic interference, and the specific Ethernet standard being used.
Higher-quality cables (e.g., Cat6, Cat6a) can support longer distances compared to lower-quality cables (e.g., Cat5e) due to their improved shielding and lower attenuation.
Gigabit Ethernet (1000 Mbps) is typically limited to the standard 100-meter distance over twisted-pair copper cables.
Yes, Ethernet transmission distances can be extended using various techniques, such as the use of fiber optic cables, Ethernet extenders, or repeaters.
Ethernet over fiber optic cables can support much longer distances, typically up to 10-40 km (6-25 miles) depending on the fiber type and Ethernet standard.
Ethernet extenders and repeaters regenerate and amplify the Ethernet signals, allowing them to be transmitted over longer distances without degradation.
Potential issues include increased latency, the need for additional power sources, and the potential for compatibility problems with certain Ethernet devices.
Yes, Ethernet protocols like Resilient Packet Ring (RPR) and Provider Backbone Bridging (PBB) have been developed to support Ethernet over wide-area networks and transport applications.
Ongoing advancements include the use of wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) over fiber, the integration of Ethernet extender functionality into network devices, and the development of new Ethernet standards for longer-reach applications.