Network cables undoubtedly play an important role in network infrastructure. This article will compare two types of network cables, STP and UTP. We will first define the basic structure and working mechanism of network cables, and outline common types of network cables, including UTP, STP, and optical fiber. Next, we will introduce the physical structure and electrical characteristics of UTP network cables, and analyze its advantages in terms of cost and flexibility.
We will explain the physical structure and electromagnetic shielding mechanism of STP network cables, and explain its advantages in terms of anti-interference and reliability. In addition, we will compare the two types of network cables in terms of transmission bandwidth, transmission distance, and anti-interference, and analyze their applicable scenarios in practical applications. Finally, we will provide the basis for selecting STP or UTP network cables based on actual needs, and explain how to balance the advantages and disadvantages of the two types of network cables in network deployment.
Basic concepts and classifications of network cables
Let me introduce you to the basic concepts and classifications of network cables.
Basic structure and working mechanism of network cable:
(1) Structure
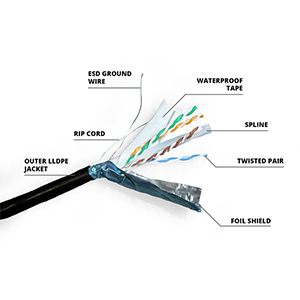
- Network cable consists of conductor, insulation layer, shielding layer and outer layer.
- Conductor is usually made of copper or aluminum wire and is used to transmit electrical signals.
- Insulation layer, shielding layer and outer layer protect and strengthen the conductor.
(2) Working mechanism
- Digital signals are transmitted through network cables, not analog signals.
- Digital signals are represented by a series of high and low levels, 1 and 0, and are used for communication between digital devices.
- The function of network cables is to reliably transmit these digital signals and connect network devices.
In summary, a network cable is a cable used for digital signal transmission. It consists of a conductor and various sheath layers and can connect different network devices.
Common types of network cables:
(1) Unshielded twisted pair (UTP)
- The most common type of network cable, without outer shielding, and low price.
- Commonly used for medium and short distance network connections, such as home and office environments.
(2) Shielded twisted pair (STP)
- On the basis of UTP, an outer copper foil or braided shielding layer is added.
- It has better anti-interference performance and is suitable for harsh environments such as industry.
(3) Fiber Optic Cable
- Using optical fiber to transmit signals can achieve long-distance high-speed transmission.
- Mainly used in backbone networks, data centers and other occasions with high bandwidth requirements.
(4) Coaxial Cable
- Using coaxial cable as the transmission medium, it is commonly used in analog video and CATV networks.
- It has strong anti-interference ability, but the transmission bandwidth and rate are relatively limited.
In short, network cables can be divided into two categories: copper cables and optical fibers according to the different transmission media, each with different performance characteristics and application scenarios.
Features of UTP (unshielded twisted pair)
Let me introduce you to the characteristics of UTP (unshielded twisted pair) network cables in detail.
Physical structure and electrical characteristics of UTP network cable:
(1) Physical structure
- UTP network cable consists of 4 pairs of twisted copper wires, each pair of wire cores is twisted into a wire.
- Each wire has a separate insulation layer, and the entire network cable is wrapped with a protective sheath.
- There is no additional shielding layer, which is what “unshielded” means.
(2) Electrical characteristics
- The characteristic impedance of UTP network cable is 100 ohms, which is suitable for 10/100/1000Mbps network.
- Due to the lack of shielding layer, UTP network cable is more sensitive to electromagnetic interference and has weak anti-interference ability.
- However, UTP cable has lower crosstalk interference and signal attenuation, and better transmission quality.
In general, the physical structure of UTP network cable is simple and there is no additional shielding layer, which determines its electrical characteristics.
Advantages of UTP network cable in terms of cost and flexibility:
(1) Cost advantage
- Due to the simple production process, the manufacturing cost of UTP network cable is low.
- Compared with STP network cable equipped with a shielding layer, UTP network cable is more affordable.
(2) Flexibility
- UTP network cable is relatively soft, easy to install and wire, and can better adapt to various environments.
- For occasions that require frequent adjustments and rewiring, UTP network cable is more flexible and convenient.
(3) Easy to disassemble and assemble
- UTP network cable connector adopts RJ-45 interface, which is easy and quick to disassemble and assemble.
- In contrast, the shielding layer of STP network cable will increase the complexity of wiring.
(4) Wide application
- Due to the above advantages, UTP network cable is widely used in small and medium-sized network environments such as home and office.
- It has become one of the most common and widely used network cable types.
In short, UTP network cable occupies a dominant position in daily network applications with its simple structure, low cost and flexible characteristics, and is one of the most popular network cable types.
Features of STP (shielded twisted pair)
Let me introduce you to the features of STP (shielded twisted pair) network cable.
STP network cable physical structure and electromagnetic shielding mechanism:
(1) Physical structure
- STP network cable adds an outer shielding layer based on UTP network cable.
- The shielding layer is usually composed of copper foil or woven metal mesh, which plays a shielding role.
- In addition, the other physical structures of STP network cable are similar to those of UTP network cable.
(2) Electromagnetic shielding mechanism
- The shielding layer can effectively isolate external electromagnetic interference and prevent it from affecting internal signals.
- It can also suppress the electromagnetic radiation generated by the internal wires to avoid interference with surrounding equipment.
- This bidirectional shielding performance makes STP network cable have stronger anti-interference ability.
In general, STP network cables achieve effective isolation from electromagnetic interference in terms of physical structure by adding an outer shielding layer.
Advantages of STP network cables in terms of anti-interference and reliability:
(1) Anti-interference
- The shielding layer can effectively suppress the impact of external electromagnetic interference on the transmission signal.
- Even in harsh industrial environments, STP network cables can maintain high transmission quality.
(2) Signal integrity
- The shielding layer can reduce the attenuation and distortion of the signal during transmission.
- Thereby ensuring the integrity and reliability of the signal, especially suitable for high-speed networks.
(3) Safety
- The outer shielding layer can effectively isolate the electromagnetic radiation of the internal wire.
- Avoid signal leakage and eavesdropping, and improve network security.
(4) Anti-interference
- The shielding layer of STP network cables can withstand large electromagnetic radiation and electrostatic pulses.
- Compared with UTP network cables, STP network cables have higher anti-interference and reliability.
In summary, STP network cables have obvious advantages in anti-interference, signal integrity, security, etc. due to the unique advantages of the outer shielding layer, and are particularly suitable for application scenarios with high reliability requirements.
Comparison of STP and UTP network cable performance
Let me compare the differences in performance indicators and applicable scenarios between STP (shielded twisted pair) and UTP (unshielded twisted pair) network cables.
Comparison of performance indicators:
(1) Transmission bandwidth
- Both STP and UTP cables can support a transmission rate of 10/100/1000Mbps.
- The bandwidth performance of the two cables is not much different, and both can meet the general network application requirements.
(2) Transmission distance
- STP cables can maintain signal quality over a longer distance due to their shielding layer.
- Generally, the maximum transmission distance of STP cables can reach 100 meters, which is slightly better than that of UTP cables.
(3) Anti-interference
- STP cables have an outer shielding layer that can effectively isolate electromagnetic interference.
- In contrast, UTP network cables have weaker anti-interference performance due to the lack of shielding.
(4) Crosstalk interference
- STP network cables have lower crosstalk interference between pairs due to the shielding layer.
- UTP network cables have relatively greater crosstalk interference between pairs due to the lack of shielding.
In general, STP network cables have a slight advantage in transmission distance and anti-interference performance, but the difference between the two in bandwidth performance is not significant.
Comparison of actual application scenarios:
(1) General office/home environment
- UTP network cables are more suitable because of their low cost and flexible wiring.
- This type of environment has lower requirements for anti-interference performance, and UTP network cables can meet the needs.
(2) Industrial/Harsh Environments
- STP cables are more suitable, and their excellent anti-interference performance is critical.
- Industrial sites have strong electromagnetic interference, and STP cables can provide more reliable transmission.
(3) High-speed Networks/Data Centers
- STP cables are more advantageous in these situations where reliability and signal integrity are required.
- With better anti-interference and longer transmission distance, STP cables can provide more stable network connections.
In short, UTP cables are more suitable for general office and home application scenarios due to their cost advantages, while STP cables are more suitable for industrial environments and high-speed networks, which require higher reliability. The two types of cables have their own characteristics, and the appropriate product should be selected according to actual needs.
Suggestions on the selection of STP and UTP network cables
I will provide you with some suggestions on how to choose STP and UTP network cables, and how to balance the advantages and disadvantages of the two types of network cables in network deployment.
Basis for choosing STP or UTP network cables:
(1) Environmental factors
- If deployed in an industrial environment or harsh environment with strong electromagnetic interference, STP network cables should be used first.
- Its excellent anti-interference performance can ensure the reliability of network connection.
(2) Transmission distance
- If data needs to be transmitted over a longer distance, STP network cables are more suitable due to their longer transmission distance.
- UTP network cables are prone to signal quality degradation over longer distances.
(3) Application requirements
- For general office or home network environments, UTP network cables can usually meet the needs.
- For high-speed networks, data centers and other occasions with higher requirements, STP network cables will be more suitable.
(4) Cost factors
- If cost is the primary consideration, UTP network cables will be more suitable due to their lower price.
- However, if reliability and anti-interference are the primary goals, the cost of STP network cables is worth it.
Based on the above aspects, you can choose the appropriate STP or UTP network cable according to your actual needs.
Suggestions for taking into account the advantages and disadvantages of both types of network cables in network deployment:
(1) Partitioned deployment
- STP network cables can be deployed in important devices or key areas to improve reliability.
- Other areas use lower-cost UTP network cables to improve overall economic efficiency.
(2) Use transition equipment
- At the junction of STP and UTP network cables, transition equipment such as shielded converters can be used.
- Ensure that signal transmission between the two types of network cables will not cause problems due to shielding differences.
(3) Reasonable wiring
- Try to shorten the wiring length of STP network cables and take advantage of their long-distance transmission advantages.
- Use UTPNetwork cables are used for medium and short distance connections, and they are flexible and economical.
(4) Monitoring and maintenance
- Regularly check the performance indicators of STP and UTP network cables to find and solve problems in a timely manner.
- Focus on the STP network cable segments that are susceptible to interference to ensure the continuous and stable operation of the network.
In short, in actual network deployment, STP and UTP network cables should be reasonably selected according to the specific environment and demand characteristics, and corresponding deployment strategies should be adopted to give full play to the respective advantages of the two types of network cables.
Summary
The reasonable selection and deployment of STP or UTP network cables is crucial for high-performance and reliable network infrastructure. Our company has long focused on the research and development and production of network equipment and its supporting products, and has rich industry experience. Our STP and UTP network cable products have reached the industry-leading level in terms of transmission performance and anti-interference ability, and can meet your demanding needs for network infrastructure construction.
Whether you need to deploy STP or UTP network cables in a telecom operator network, data center, or enterprise LAN, we can provide you with customized solutions. At the same time, our professional team will provide you with a full range of technical support, including on-site surveys, solution design, and equipment installation and maintenance. Contact us now to learn more about the application of STP and UTP network cables.
Differences between STP and UTP cables FAQ
STP cable has a metallic shield around each individual twisted pair of copper wires to provide protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk.
UTP cable has no metallic shielding around the twisted pairs of copper wires. It relies on the twisted pair design alone to reduce electromagnetic interference.
The metallic shielding in STP cable acts as a Faraday cage, blocking external electrical and magnetic fields from interfering with the data signals.
STP cable provides better protection against EMI/RFI, reduced crosstalk, and improved signal integrity, making it more suitable for noisy environments.
STP cables are generally more expensive, heavier, and more difficult to install compared to UTP cables due to the additional shielding.
STP is commonly used in industrial, medical, and other settings with high electromagnetic interference, while UTP is more common in office and home networks.
STP is often used in industrial Ethernet, audio/video, and other applications requiring superior noise immunity. UTP is widely used in Ethernet LAN and telephone networks.
STP cables can typically transmit signals for longer distances than UTP, up to 100 meters for Gigabit Ethernet.
While they use the same RJ-45 connectors, STP and UTP cables are not directly interchangeable due to the differences in construction.
Proper grounding of the STP cable’s metallic shield is crucial to provide the intended electromagnetic protection.