Wide Area Networks (WANs) play an important role in networking. However, WANs also have some disadvantages and limitations. This article will focus on the three main disadvantages of WANs: high cost, slow network speed, and low reliability. We will first review the basic concepts and application scenarios of WANs.
Next, we will analyze the causes of these three disadvantages and explain their impact on WAN deployment and use. For example, high costs limit the deployment of small businesses or individual users, slow networks affect the quality of real-time applications and video services, and low reliability leads to business interruptions and reduced user expectations.
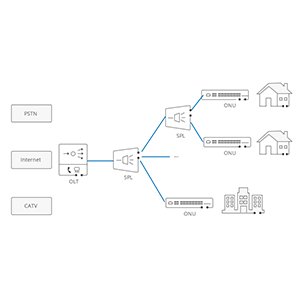
The concept of Wide Area Network (WAN)
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a network that covers a wide geographical area and connects multiple locations or networks. It supports long-distance data transmission and cross-regional communication, usually using transmission media such as optical fiber, satellite, or wireless links, and is suitable for enterprises, data centers, and global Internet connections.
Basic features of WAN:
A wide area network (WAN) is a computer network with a wide coverage area. Its main features include:
(1) Wide geographical coverage:
- WAN can connect long-distance networks across the geographical boundaries of cities, provinces, and even countries.
- It is not limited to a building or campus like a local area network (LAN).
(2) Connect across large distances:
- WAN links can connect locations that are far apart, such as hundreds or thousands of kilometers away.
- This requires the use of long-distance transmission media such as dedicated lines and optical fibers to achieve the connection.
WAN applications in enterprises and other fields:
WAN is widely used in enterprise networks and other fields, mainly in the following aspects:
(1) Connecting headquarters and branches:
- Enterprises can use WAN technology to connect branches in different locations with the headquarters.
- This can achieve cross-regional information sharing and business collaboration.
(2) Supporting cloud services and data center interconnection:
- WAN provides enterprises with the ability to access remote cloud computing resources and data centers.
- Through WAN connections, enterprises can make full use of cloud services and computing resources in remote data centers.
In short, with its wide geographical coverage and long-distance connection capabilities, WAN plays a key role in enterprise network construction and other field applications, and is one of the important infrastructures of modern information society.
The first major disadvantage of WAN: high cost
The first major disadvantage of WAN is its high cost, including equipment purchase, installation and maintenance costs. WANs usually rely on dedicated lines or high-bandwidth transmission media, which may lead to high operating and management costs.
Cost factors for WAN construction and operation and maintenance:
The main cost factors for WAN construction and operation and maintenance include:
(1) Leased circuit rental fees:
- WANs usually require the use of dedicated circuits provided by telecommunications operators, such as optical fiber, T1 lines, etc.
- The rental and use fees of these dedicated circuits are the main expenses of WAN construction.
(2) Investment in network equipment and management personnel:
- WAN deployment requires network equipment such as routers and switches, as well as professional network management personnel.
- These hardware and labor costs are also an important part of WAN operation.
The impact of high costs on WAN deployment:
The high cost of WAN construction and operation and maintenance will have the following impacts on WAN deployment and application:
(1) Restricting deployment by small enterprises or individual users:
- The high cost of WAN construction is often beyond the budget of small and medium-sized enterprises or individual users.
- This cost barrier limits the popularity of WAN among small user groups.
(2) Increasing the difficulty of WAN maintenance and expansion:
- High costs mean that WAN maintenance and expansion require more investment.
- This may reduce the enthusiasm of enterprises or organizations to expand WAN networks.
In short, the high cost of WAN construction and operation is an important challenge it faces. This shortcoming also limits the popularity and development of WAN in certain application scenarios. Therefore, how to control and reduce WAN costs is a key issue that requires continuous attention and improvement.
The second major disadvantage of WAN: slow network speed
The second major disadvantage of WAN is slow network speed, especially in remote connections and high traffic conditions. Long-distance data transmission and shared bandwidth may cause delays and bandwidth bottlenecks, thereby affecting overall network performance and response speed.
Reasons for slow WAN speed:
The network speed of a wide area network (WAN) is usually slower than that of a local area network (LAN), mainly due to the following two reasons:
(1) Limited physical line transmission bandwidth:
- WAN usually uses lower bandwidth transmission lines, such as telephone lines, satellite links, etc.
- The bandwidth of these physical lines is limited, which limits the transmission speed of WAN.
(2) Forwarding through multiple network devices:
- WAN data packets need to be forwarded through multiple routers, switches and other devices.
- The processing and forwarding of each device will increase the delay, resulting in a decrease in the overall network speed.
The impact of slow network speed on user experience:
The slow WAN speed will have the following negative impacts on user experience:
(1) Affecting the quality of real-time applications and video services:
- Real-time applications, such as video conferencing and online games, have high requirements for network speed.
- Slow network speed will cause such applications to experience problems such as freezes and delays, affecting user experience.
(2) Improve user expectations of network performance:
- With the development of Internet applications, users have higher and higher requirements for network speed and response time.
- Slower WAN speeds are difficult to meet users’ ever-increasing performance expectations.
In general, the slower WAN speed is another important disadvantage it faces, which not only affects the performance of some applications, but also increases users’ expectations of network performance. Solving the WAN speed problem is the key to improving the quality of WAN services.
The third major disadvantage of WAN: low reliability
The third major disadvantage of WAN is low reliability. Because it relies on public or remote transmission media, it may be affected by network failures, signal interference and link interruptions, resulting in unstable data transmission and reduced network availability.
Reasons for weak WAN network reliability:
The network reliability of a wide area network (WAN) is usually lower than that of a local area network (LAN), mainly for the following reasons:
(1) High risk of single point failure:
- A WAN consists of network devices and transmission lines in multiple locations.
- Any failure of a key device or link may cause the entire WAN to be interrupted.
(2) Complex remote maintenance and troubleshooting:
- A WAN spans multiple geographical locations, and network management personnel cannot directly reach the site for maintenance.
- Remote diagnosis and troubleshooting will increase repair time and affect reliability.
The impact of low reliability on business continuity:
The low reliability of WAN networks will have the following negative impacts on the business continuity of enterprises:
(1) Network interruption will lead to interruption of enterprise production:
- WAN interruption means that cross-regional business collaboration and information sharing will also be interrupted.
- This may lead to the temporary suspension of enterprise production and operation activities.
(2) Users’ expectations for network services increase:
- With the continuous improvement of informatization, users’ expectations for the reliability of network services are also getting higher and higher.
- For some key business applications, users cannot tolerate network interruptions.
In short, the low reliability of WAN networks is an important disadvantage. This will not only bring interruption risks to enterprise production and operations, but also make it difficult to meet users’ expectations for network services. Improving WAN reliability is a continuous goal of network construction and operation and maintenance.
Summary
Although WAN has some shortcomings, it still plays an indispensable role in supporting modern network applications. Our company has long been committed to developing innovative WAN solutions to overcome the above limitations and provide users with high-performance and highly reliable WAN services.
Our WAN products use industry-leading technologies to effectively reduce deployment and operation and maintenance costs and improve network speed and reliability. At the same time, our team of engineers will provide you with professional demand analysis and solution design services, and customize WAN solutions that meet your needs according to your specific situation. Contact us now to learn more.
About WAN Disadvantages FAQ
Common disadvantages of WAN include higher costs, complex setup and management, potential security risks, variable performance, and dependency on external service providers.
WANs are typically more expensive due to the costs associated with long-distance data transmission, higher service fees from ISPs, and the need for specialized equipment and infrastructure to maintain and manage the network.
WAN setup and management can be complex due to the need for configuring multiple network devices, coordinating with ISPs, managing various types of connections, and ensuring consistent performance across different geographic locations.
WANs can be more vulnerable to security threats due to their broad scope and exposure to the internet. Potential risks include data breaches, unauthorized access, and cyberattacks. Implementing robust security measures is essential to mitigate these risks.
The performance of a WAN can be affected by distance, with increased latency and potential data loss over long distances. Network performance may degrade as data travels farther, impacting the speed and reliability of connections.
WAN performance can vary due to factors such as network congestion, bandwidth limitations, the quality of the physical connections, and the performance of intermediate networking equipment. This variability can affect data transfer speeds and overall network efficiency.
Relying on external service providers introduces risks such as service outages, varying levels of customer support, and dependency on their network infrastructure. These factors can impact the reliability and performance of your WAN connection.
WANs often experience higher latency compared to LANs due to the longer distances that data must travel and the complexity of routing through various network segments. High latency can affect real-time applications and user experience.
While WANs can scale to connect multiple locations, there are limitations related to the cost and complexity of expanding network infrastructure. Adding more connections or increasing bandwidth may involve significant investment and planning.
Maintaining a WAN involves monitoring network performance, troubleshooting issues, managing network upgrades, and ensuring security. The complexity of managing a large-scale network and coordinating with multiple service providers can be challenging.