As a key transmission medium for high-speed communication networks, optical fiber cables have attracted much attention for their protection measures. This article will focus on how to protect fiber optic cables from all types of damage. We will first introduce the characteristics and vulnerability of fiber optic cables and analyze the mechanical, environmental and electromagnetic damage factors to which they are susceptible.
Next, we will elaborate on the mechanical protection measures of optical fiber cables, including the role of outer protective materials and the impact of laying methods on protection. At the same time, we will also discuss the protection strategies of fiber optic cables in harsh environments and how to reduce electromagnetic interference through shielding and grounding. Finally, we will introduce the key points of daily maintenance of fiber optic cables and how to use condition monitoring technology to achieve active protection.
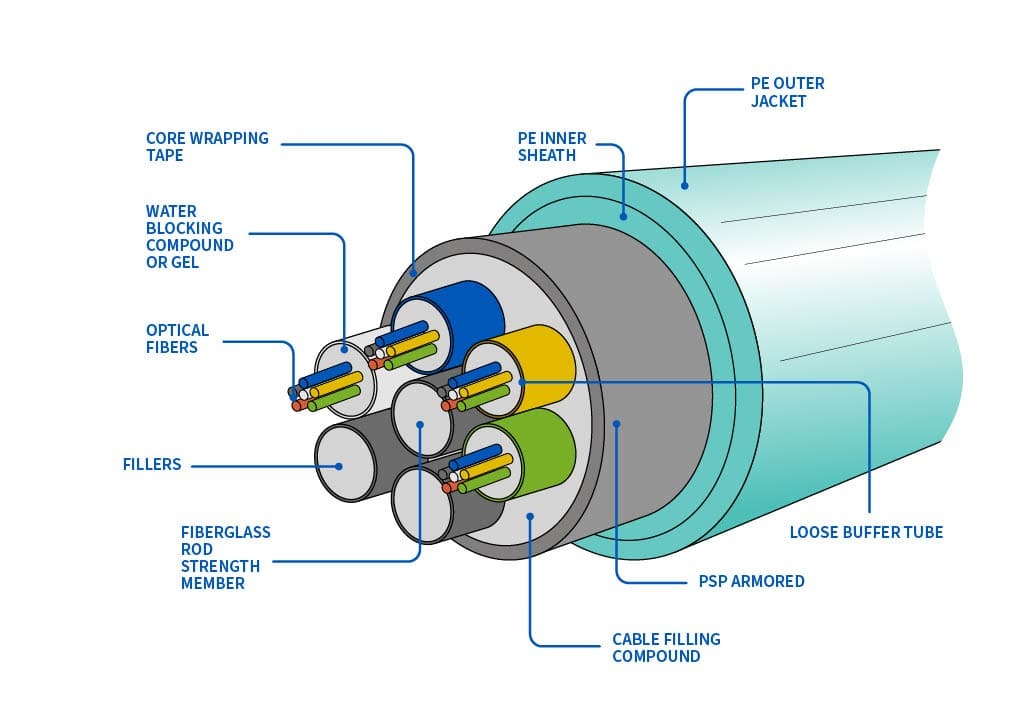
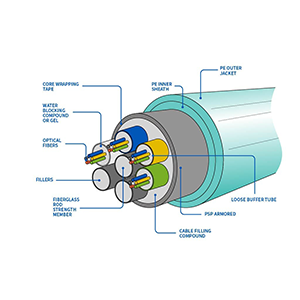
Basic overview of fiber optic cables
Let me introduce to you in detail the characteristics of fiber optic cables and the factors that are susceptible to damage:
Material composition and working principle of optical fiber cable:
- The core material of optical fiber is high-purity glass or plastic.
- Optical fiber consists of core, lining, protective layer and other parts.
- Light is transmitted inside the optical fiber through total reflection, which requires a difference in refractive index between the core layer and the lining layer.
- The protective layer prevents the optical fiber from physical damage, such as bending, stretching, etc.
Damage factors that fiber optic cables are susceptible to:
(1) Mechanical damage:
- Bend or break: Excessive bending or squeezing can cause the fiber to break.
- Stretch: Excessive pulling force will cause micro cracks and breaks in the optical fiber.
- Compression: Pressure from heavy objects will cause local deformation and breakage of the optical fiber.
(2) Damage to environmental conditions:
- Temperature: High temperatures will cause the optical fiber material to age and become brittle, while low temperatures will cause it to become brittle.
- Moisture: Long-term exposure to moisture can cause oxidation of the optical fiber surface.
- Chemical corrosion: Some chemicals can corrode the optical fiber protective layer and core materials.
(3) Installation/connection damage:
- Improper connector docking: Poor connector contact will cause signal attenuation.
- Poor welding technology: Improper welding can cause fiber breakage or increased light loss.
- Irregular installation: Improper laying of cables can cause bending or excessive tension.
(4) Other damage:
- Electromagnetic interference: High-intensity electromagnetic fields can cause fiber optic signal fluctuations.
- Animal chewing: Some animals will chew optical fibers as food and cause damage.
- Man-made damage: Accidental stepping, cuts, etc. may cause the optical fiber to break.
In short, fiber optic cables are more fragile than conventional cables due to their material properties and working principles, and are easily damaged by various mechanical, environmental and human factors. Therefore, extra caution is required during the laying, splicing and use of fiber optic cables.
Mechanical protection measures for optical fiber cables
Let me introduce to you the mechanical protection measures for fiber optic cables:
The role of outer protective materials of optical fiber cables:
- Buffer layer:
- Made of plastic material, it can absorb external pressure and reduce the impact on the fiber core.
- Improve the tensile, compression and bending resistance of optical fibers.
- Strengthening layer:
- Made of high-strength materials such as steel wire and Kevlar fiber to provide mechanical protection.
- Able to withstand large tensile, compressive and torsional forces, enhancing the overall resistance of the cable.
- Jacket:
- Usually made of PVC, polyethylene and other materials to provide external protection.
- Can prevent cables from mechanical damage such as extrusion, cuts, corrosion, etc.
The laying methods of optical fiber cables and their protective effects:
- Underground laying:
- Trenches need to be dug in the soil for burial, and sufficient burial depth and protective layer are required.
- Stronger steel tape reinforced fiber optic cables can be chosen.
- Overhead laying:
- Hung in the air by separate or common poles, it is necessary to prevent the pressure of heavy objects and the swing of wind.
- Fiber optic cables with high-strength monofilament cores can be used.
- Pipe laying:
- When laying cables in pipes, make sure there are no sharp corners or burrs in the pipes.
- You can choose compact fiber optic cables with better flexibility.
- Trench laying:
- Through special cable trench laying, it is necessary to prevent flooding and extrusion damage.
- Fiber optic cables with metal reinforcements can be used.
In short, rational selection of outer protective materials for optical fiber cables and appropriate laying methods are key measures to protect optical fibers from mechanical damage. This is critical to ensuring the reliable operation of fiber optic networks.
Environmental protection measures for optical fiber cables
Let me introduce to you in detail the protective measures for fiber optic cables in harsh environments:
Fiber optic cable resistance to temperature and humidity:
- Temperature resistance:
- Standard fiber optic cables typically withstand temperatures ranging from -20°C to 70°C.
- Special temperature-resistant fiber optic cables can withstand temperature changes from -40°C to 85°C.
- Humidity Resistance:
- Standard fiber optic cables can withstand environments with up to 95% relative humidity.
- Moisture resistance can be improved by strengthening the outer sheath and sealing measures.
Protective measures for optical fiber cables in harsh environments:
(1) High temperature environment:
- Choose high-temperature-resistant optical fiber cables, such as quartz glass core or metal-reinforced outer sheath.
- Leave enough margin when laying cables to prevent stress caused by thermal expansion and contraction.
- Use passive or active ventilation and cooling measures when necessary.
(2) Low temperature environment:
- Choose optical fiber cables that are still flexible at low-zero temperatures, such as polyethylene outer sheaths.
- Avoid excessive bending radius when laying cables to prevent them from becoming brittle and breaking at low temperatures.
- Cable heating or insulation can be used to maintain the cable temperature within an appropriate range.
(3) Humid environment:
- Choose optical fiber cables with waterproof properties, such as metal sheaths or sealed designs.
- When laying cables, pay attention to preventing moisture intrusion, such as taking sealing and drainage measures.
- Regularly check the cables for condensation, water immersion, etc., and take remedial measures in a timely manner.
(4) Chemical environment:
- Choose chemically resistant fiber optic cables, such as polyamide or fluoroplastic.
- Avoid contact with corrosive substances such as acids, alkalis, organic solvents, etc. when laying cables.
- If necessary, adopt isolation protection, such as using metal pipes or protective boxes.
In short, in view of different harsh environmental factors, it is necessary to rationally select the material and structural design of optical fiber cables, and take appropriate laying and protection measures to ensure the long-term stable operation of optical fiber networks.
Electromagnetic protection measures for optical fiber cables
Let me introduce to you the electromagnetic protection measures of optical fiber cables in detail:
Vulnerability of fiber optic cables to electromagnetic interference:
- The optical fiber cable itself is an insulating material without metal conductors and does not produce electromagnetic induction.
- However, strong external electromagnetic fields may pass through the insulation layer of fiber optic cables and induce weak signal interference.
- This electromagnetic interference can cause distortion, jitter, or even complete loss of optical signals.
- Therefore, optical fiber networks will face greater challenges in some strong electromagnetic environments (such as near high-voltage lines).
Shielding and grounding measures for optical fiber cables:
(1) Blocking measures:
- Add a metal braid or metal foil layer to the outer layer of the optical fiber cable to form an electromagnetic shielding layer.
- The shielding layer can effectively block the interference of external strong electromagnetic fields on optical fiber signals.
- For special applications, double or triple shielding designs can also be used to improve anti-interference.
(2) Grounding measures:
- Ground the shielding layer reliably to form a low-impedance ground loop.
- This can quickly conduct the intruding electromagnetic interference current away through the ground wire to avoid interference transmission.
- The grounding method can be single-point grounding or multi-point grounding, selected according to the specific application scenario.
(3) Other auxiliary measures:
- When selecting an optical fiber transceiver, its anti-interference performance should also be considered.
- For key parts, photoelectric isolation technology can also be used to further improve anti-interference capabilities.
- Properly plan the layout of optical fiber lines and keep them away from strong electromagnetic sources such as high-voltage lines and substations.
In short, through the comprehensive application of shielding, grounding and other auxiliary measures, the anti-interference performance of optical fiber cables in strong electromagnetic environments can be effectively improved to ensure the safe and stable operation of optical fiber networks.
Maintenance and monitoring of fiber optic cables
Let me introduce you to the routine maintenance and monitoring techniques of fiber optic cables:
Daily inspection and maintenance of fiber optic cables:
(1) Regular inspection:
- Check whether the cable has any appearance damage, such as breakage, bending, indentation, etc.
- Check whether the connector connection is firm and whether it is loose or falling off.
- Check the cable laying environment for abnormal conditions such as accumulation of debris, moisture, heat, etc.
(2) Cleaning and maintenance:
- Clean the cable surface regularly to remove dust, stains and other impurities.
- Clean the joint surface and keep it clean and dry.
- If necessary, tools such as dust-free paper and alcohol can be used for cleaning.
(3) Preventive maintenance:
- Repair any mechanical damage found, such as breakage, bending, etc. in a timely manner.
- Regularly check the integrity of the cable protective layer and replace damaged parts in a timely manner.
- Regularly check and supplement cable protective measures according to the usage environment.
(4) Emergency response:
- Once a serious fault is discovered, emergency measures should be taken immediately to isolate or repair it.
- Develop a detailed emergency plan and clarify the division of responsibilities and maintenance procedures.
- Spare cables and repair tools should be readily available to facilitate quick response.
Fiber optic cable condition monitoring technology:
- Optical Time Domain Reflectometry (OTDR):
- Can detect fiber core continuity, splice point loss, line bending and other conditions.
- Accurately locate fiber fault points by analyzing the reflection characteristics of light pulses.
- Optical power meter/light source:
- The total attenuation value of the optical fiber link can be measured to find the deterioration of the link transmission performance.
- Used with OTDR, it can comprehensively diagnose the transmission quality of optical fiber cables.
- Fiber optic sensing technology:
- Use the optical fiber itself as a sensor to monitor cable stress, temperature, humidity, etc.
- Provides early warning of mechanical and environmental damage to fiber optic cables.
In short, daily inspection and maintenance of optical fiber cables, as well as advanced condition monitoring technology, are key safeguards to ensure the reliable operation of optical fiber networks.
Summary
Protecting fiber optic cables from all types of damage is key to ensuring the stable operation of high-speed communication networks. Our company has long been focused on the research and development of optical fiber cables and their protection technology, and has rich industry experience. Our fiber optic cables not only use high-quality outer protective materials that provide excellent resistance to mechanical, environmental and electromagnetic interference, but are also equipped with advanced condition monitoring systems that enable active protection.
No matter how harsh your fiber optic cable deployment environment is, we can provide you with customized solutions to ensure the long-term stable and efficient operation of your communication network. at the same time, our professional team is ready to provide you with a full range of technical support and maintenance services to help you build an excellent optical fiber communication infrastructure. Contact us today to learn more about our fiber optic cable protection products and services.
Fibre Optic Cable FAQ
Fiber optic cables can be vulnerable to damage from factors like bending, crushing, stretching, moisture, and exposure to chemicals or rodents.
The main principles are to minimize physical stress on the cable, isolate it from environmental hazards, and provide redundancy or backup options.
Protective measures include using cable trays or conduits, installing the cables in underground ducts or trenches, and applying additional outer jackets or armor.
Ensuring proper cable routing, maintaining minimum bend radii, and using cable supports or management systems can help prevent fiber damage from bending or crushing.
Measures include using waterproof cable jackets, sealants, and glands, as well as installing the cables in waterproof conduits or enclosures.
Common approaches involve using rodent-resistant cable designs, physical barriers, and deterrents like chemical repellents or ultrasonic devices.
Careful handling, the use of protective sheaths, and controlled splicing environments are important to prevent damage during installation.
Factors like environmental exposure, soil conditions, and potential construction activities require specific protection measures.
Techniques include continuous cable monitoring, regular inspections, and the use of fiber optic test equipment to detect any issues.
Standards from organizations like the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) provide guidance on proper fiber optic cable protection.