Thank you for choosing to read this article. Today I will introduce to you EPON (Ethernet Passive Optical Network) optical fiber and its important role in optical fiber communication. EPON optical fiber is a high-bandwidth, high-speed solution that provides superior performance and reliability for modern network connections.
Overview of EPON optical fiber
EPON (Ethernet Passive Optical Network) optical fiber is a passive optical fiber network based on Ethernet technology, which plays an important role in optical fiber communication. The following is an overview of EPON fiber:
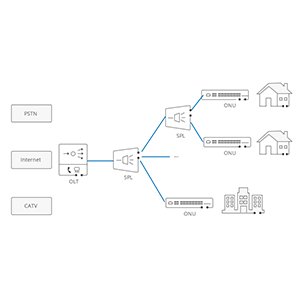
EPON optical fiber is a solution based on optical fiber transmission, which uses optical fiber as the transmission medium and uses the Ethernet protocol for data transmission. EPON fiber optic networks usually consist of optical line terminals (OLT) and optical network units (ONU). The OLT serves as a central device connected to the service provider’s core network, while the ONU connects to user devices such as computers, IP phones, cameras, etc. in homes, businesses, or institutions.
The role of EPON optical fiber is to provide high-bandwidth and high-speed data transmission. It transmits data through optical fiber, has larger bandwidth and higher transmission rate, and can meet the needs of modern applications for large-scale data transmission. The working principle of EPON optical fiber is to convert data packets into optical signals, transmit them to the destination through the optical fiber, and then convert the optical signals back into data. This transmission method enables EPON optical fiber to provide high-speed data transmission and stable connections.
The working principle of EPON optical fiber
The working principle of EPON optical fiber involves multiple key components, including optical fiber transmission, optical modules, OLT (Optical Line Terminal) and ONU (Optical Network Unit). The following are the basic principles of EPON fiber:
-
Optical fiber transmission: EPON optical fiber uses optical fiber as the transmission medium. Optical fiber is a slender glass or plastic material with a high refractive index that transmits light signals through internal reflections of light. Optical fiber can carry large amounts of data and has the characteristics of low attenuation, low interference and high bandwidth.
-
Optical module: Optical module is one of the key components in EPON optical fiber. The optical module is responsible for converting electrical signals into optical signals and sending the optical signals into optical fibers for transmission. At the transmitting end, the optical module receives the electrical signal from the OLT, converts it into an optical signal and sends it through the optical fiber. At the receiving end, the optical module receives the optical signal from the optical fiber and converts it into an electrical signal and sends it to the ONU.
-
OLT (Optical Line Terminal): OLT is the central device of the EPON optical fiber network and is responsible for managing and controlling the entire optical fiber network. The OLT is connected to the service provider’s core network and communicates with multiple ONUs. It is responsible for transmitting data to the correct ONU and manages functions such as bandwidth allocation, data transmission scheduling and network security.
-
ONU (Optical Network Unit): ONU is a terminal device in the EPON optical network and is connected to user equipment. Each ONU is usually connected to one or more user devices, such as computers, IP phones, cameras, etc. The ONU receives optical signals from optical fibers and converts them into electrical signals for use by user equipment. The ONU is also responsible for communicating with the OLT and transmitting data sent by the user equipment to the OLT.
Technical specifications of EPON optical fiber
The technical specifications of EPON (Ethernet Passive Optical Network) optical fiber define its transmission rate, fiber interface type, transmission distance and other parameters. The following are the general technical specifications of EPON fiber:
-
Transmission rate: EPON optical fiber usually provides a transmission rate of 1 Gbps (Gigabits per second), which means it can transmit 1 billion bits per second. However, there are also EPON optical fibers that support high-speed transmission of 10 Gbps.
-
Optical fiber interface type: The type of optical fiber interface used by EPON optical fiber is usually the standard SC (Subscriber Connector) or LC (Lucent Connector). These interface types have good compatibility and can be easily connected to optical modules or other optical fiber equipment.
-
Transmission distance: The transmission distance of EPON optical fiber can vary according to different specifications and implementation methods. Usually, the transmission distance of EPON optical fiber can reach more than 20 kilometers, and some implementations can even reach 60 kilometers.
It should be noted that EPON and GPON, as different optical fiber standards, have different adoption situations in different markets and applications. The specific choice of fiber optic standard depends on specific needs and application scenarios.
Application scenarios of EPON optical fiber
EPON (Ethernet Passive Optical Network) optical fiber has a wide range of application scenarios in different network environments, especially in broadband access, enterprise networks and mobile communications. The following are some main application scenarios of EPON fiber:
-
Broadband access: EPON optical fiber plays an important role in the field of broadband access. It can provide high-speed, stable Internet access and meet the needs of home and business users for large bandwidth. EPON optical fiber’s high-bandwidth transmission and flexible scalability make it an ideal choice for providing broadband access.
-
Enterprise network: EPON optical fiber is also commonly used in enterprise networks. EPON optical fiber can provide enterprises with high-speed and reliable data transmission, supporting large-scale data exchange, video conferencing, cloud computing and other network applications. The high bandwidth and low latency characteristics of EPON optical fiber enable enterprises to build powerful network infrastructure to meet growing business needs.
-
Mobile communications: The application of EPON optical fiber in the field of mobile communications is also gradually increasing. With the rapid growth of mobile data traffic, mobile operators need reliable, high-bandwidth transmission networks to support mobile communication services. EPON optical fiber can provide high-speed data transmission and backhaul transmission for mobile communication base stations to meet the capacity needs of mobile networks.
In short, the application of EPON optical fiber in fields such as broadband access, enterprise networks and mobile communications is growing. Its high bandwidth, stability and scalability make it an important choice to meet the needs of modern networks, providing users with fast and reliable data transmission and connections.
Advantages and challenges of EPON optical fiber
EPON (Ethernet Passive Optical Network) optical fiber has some advantages compared with other access technologies, but there are also some challenges. The following is an analysis of the advantages and challenges of EPON fiber:
Advantage:
-
High bandwidth: EPON optical fiber provides high-speed data transmission capabilities and can meet users’ needs for large bandwidth. It supports high-speed uplink and downlink transmission rates, providing users with fast Internet access and data transmission experience.
-
Flexibility: EPON optical fiber adopts Ethernet protocol and is compatible with existing Ethernet technology. This compatibility makes EPON optical fiber flexible in terms of access equipment and can be integrated with various Ethernet devices and protocols without changing the existing network infrastructure.
-
Cost-effectiveness: Compared with other optical fiber access technologies, EPON optical fiber usually has a lower cost. EPON fiber is relatively low-cost to deploy and maintain because it uses common Ethernet technology and standard fiber interfaces, requiring no special equipment or infrastructure.
-
Scalability: The network architecture of EPON optical fiber supports a large number of user connections and has good scalability. This means that the network can easily accommodate growth in the number of users and can flexibly allocate bandwidth resources.
challenge:
-
Optical fiber cabling: The deployment of EPON optical fiber requires optical fiber cabling work, which may require a certain amount of time and cost. In particular, fiber optic cabling in existing buildings or infrastructure can present difficulties and the adaptability and feasibility of the cabling need to be taken into consideration.
-
Equipment compatibility: EPON optical fiber needs to be compatible with equipment such as optical modules, OLT (Optical Line Terminal) and ONU (Optical Network Unit). When implementing an EPON network, you need to ensure the compatibility of the selected equipment to ensure the proper operation and performance of the network.
-
Technology maturity: Compared with other access technologies (such as ADSL or GPON), EPON has relatively few applications worldwide. This may result in limited technical support and maintenance resources in some regions and among suppliers, and may face some challenges in the deployment and maintenance of EPON networks.
It is important to note that the advantages and challenges of EPON fiber may vary in different environments and implementations. When implementing an EPON network, these factors need to be considered comprehensively and appropriate solutions developed based on specific circumstances.
The future development trend of EPON optical fiber
EPON optical fiber has potential in future network development and has some development trends to meet the growing network needs and expansion requirements. The following are some important trends in the future development of EPON optical fiber:
-
Higher bandwidth requirements: With the continuous growth of digital content, high-definition video, virtual reality, Internet of Things, cloud computing and other applications, users’ demand for bandwidth will continue to increase. EPON optical fiber has the ability to provide high bandwidth and can meet future demand for higher-speed transmission.
-
5G and mobile communications: The rapid development of 5G networks will bring more demands for mobile communications. EPON optical fiber, as the post-transmission network of the 5G network, can provide high-speed, low-latency data transmission and support large-scale mobile communications and data traffic.
-
Fiber to the home (FTTH) and fiber to the building (FTTB): The deployment of FTTH and FTTB will continue to expand to provide higher quality Internet access and broadband services. EPON optical fiber will continue to play an important role in these areas as a cost-effective and flexible solution.
-
Low power consumption and green environmental protection: As the focus on energy efficiency and environmental sustainability increases, the advantages of EPON optical fiber in low power consumption and green environmental protection will receive more attention.
Summarize:
The future development trend of EPON optical fiber is very broad. With the rise of emerging technologies and applications, such as 5G networks, Internet of Things and cloud computing, EPON optical fiber will play a more important role. It has the potential to meet future network needs and expansion, providing an excellent solution for building high-speed, reliable network connections.
If you are interested in EPON optical fiber, please consider contacting us. We will provide you with professional advice and support to help you choose an EPON optical fiber solution that suits your needs and achieve high-bandwidth and high-speed network communications.
- What is a fiber EPON?
- Which is better EPON or GPON?
- What is EPON and GPON standards?
- How do you identify GPON and EPON?
- What is EPON ONU?
- What are the components of EPON?
- What are the advantages of EPON?
- Where is EPON used?
- Is GPON the same as fiber?