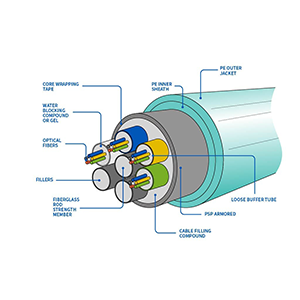
I am pleased to introduce you to SFP optical cable, a high-performance optical fiber cable used to connect optical modules and network equipment. SFP optical cable adopts hot-pluggable SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable) interface to provide you with flexible and reliable optical fiber connection solutions.
SFP optical cable supports a variety of optical fiber types, including single-mode fiber (SMF) and multi-mode fiber (MMF). You can choose the appropriate optical cable according to your needs. They have different transmission distances and rates, and can support transmission rates up to 10Gbps, 40Gbps and 100Gbps.
Introduction to SFP cables
Definition and background:
SFP optical cable is an optical fiber cable used to connect optical modules and network equipment. The full name of SFP optical cable is Small Form-Factor Pluggable optical cable, which originated from the standardization of SFP interface. The SFP interface is a hot-swappable module interface used to connect optical fibers and copper cables, making the connection between optical modules and network equipment more flexible and convenient.
SFP interface:
The SFP interface is a small optical module interface, also called a Mini-GBIC (Gigabit Interface Converter) interface. It has the following characteristics and functions:
-
Miniaturized size: The SFP interface adopts a miniaturized size design, which is usually smaller than the previous optical module interface. This miniaturized design enables a higher density of optical modules, allowing more optical fibers to be connected in a limited space.
-
Hot-swappable capability: The SFP interface supports hot-swappable functionality, allowing the SFP optical module to be inserted or removed while the device is running. This means that optical modules can be replaced or upgraded without interrupting network services, improving the maintainability and flexibility of the network.
-
Versatility: The SFP interface supports multiple types of SFP optical modules, including fiber optic modules (such as SFP-SX, SFP-LX, SFP-LR, etc.) and copper cable modules (such as SFP-T). This enables the SFP interface to adapt to different network needs and media types.
-
High-speed transmission: SFP interfaces are usually used to support high-speed transmission, including 1Gbps, 10Gbps and other rates. This makes SFP optical cables ideal for transmitting data in high-speed network environments.
Types and specifications of SFP cables
Fiber type:
SFP optical cable can support different types of optical fibers, mainly including single-mode fiber (Single Mode Fiber, SMF) and multi-mode fiber (Multi-Mode Fiber, MMF).
-
Single-mode fiber (SMF): SMF is suitable for long-distance transmission, its core diameter is small (usually 9μm), and the optical signal is transmitted in a single mode in the fiber. SMF is usually used in applications requiring longer transmission distances and higher bandwidth.
-
Multimode fiber (MMF): MMF is suitable for short-distance transmission, its core diameter is larger (usually 50μm or 62.5μm), and the optical signal is transmitted in multiple modes in the fiber. MMF is typically used in applications requiring shorter transmission distances and lower bandwidth.
Length and rate:
The length and supported transmission rates of SFP optical cables depend on the specific SFP optical module specifications and standards. Here are some examples of common SFP fiber optic cable rates and transmission distances:
-
1Gbps (gigabits per second): For 1Gbps SFP optical cable, the transmission distance usually supported ranges from tens to hundreds of meters, depending on the fiber type used (SMF or MMF) and the optical module specifications.
-
10Gbps (gigabits per second): SFP optical cable used for 10Gbps, which usually supports transmission distances ranging from tens of meters to tens of kilometers. For shorter distance transmission, MMF fiber can be used, while for longer distance transmission, SMF fiber is required.
-
40Gbps and 100Gbps: For higher-rate SFP optical cables, such as 40Gbps and 100Gbps, special optical modules and fiber types are usually required, such as 40GBASE-SR4, 40GBASE-LR4, 100GBASE-SR4, 100GBASE-LR4, etc. These optical cables can support longer transmission distances, for example, 40GBASE-LR4 optical cables can support a transmission distance of 10 kilometers.
It should be noted that the specific SFP optical cable specification and supported transmission distance and rate depend on the optical module and manufacturer used. When selecting SFP optical cables, the selection should be based on actual needs and the specifications and requirements of the optical module.
Connection and application of SFP cables
data center:
In data centers, SFP optical cables are widely used in scenarios such as connections between servers and interconnection of network switches and routers. Here are some of the major applications of SFP fiber optic cables in data centers:
- Server interconnection: Servers in data centers often require high-speed connections for data exchange and communication. SFP optical cables can be used to connect optical modules between servers to achieve high-speed and reliable data transmission.
-Interconnection of network switches and routers: Network switches and routers in data centers need to be interconnected to build a large-scale data center network. SFP optical cables can be used to connect different devices to interconnect and expand data center networks.
- Storage network (SAN) connection: In data centers, storage devices usually need to be connected to servers to achieve efficient storage management and data access. SFP optical cables can be used to connect optical modules between storage devices and servers to build a SAN environment.
Teleworking and campus networking:
In addition to data centers, SFP optical cables also play an important role in remote offices and campus networks. The following are the applications of SFP optical cables in these scenarios:
-
High-speed connections between buildings: In corporate office buildings, within campuses, or between campuses, high-speed, reliable connections are needed to realize data exchange and communication between various areas. SFP optical cables can be used for optical fiber connections between buildings to provide high-speed data transmission.
-
Remote data transmission: In remote offices and campus networks, data sometimes needs to be transmitted over longer distances. Some types of SFP optical cables, such as SFP-LR (Long Range) modules, can support data transmission within a range of tens of kilometers, providing reliable long-range data connections.
-
Network expansion and upgrades: As remote offices and campus networks develop, network size and bandwidth requirements may gradually increase. The hot-swappable capability of SFP optical cables makes network expansion and upgrades more flexible and convenient. Optical modules can be replaced or upgraded as needed to meet growing network needs.
Advantages and considerations of SFP cables
Flexibility and scalability:
SFP optical cable provides flexibility and scalability in network design because:
-
Interchangeability: SFP optical cables use standardized optical module interfaces, making SFP optical modules of different types and specifications interchangeable. This means that suitable SFP optical modules can be selected according to actual needs, including different transmission rates, supported fiber types and transmission distances, etc. This replaceability makes network design more flexible and can be adjusted and upgraded according to different application scenarios.
-
Upgradeability: Since SFP optical cable supports hot-swappable function, network administrators can replace or upgrade SFP optical modules at any time without interrupting network services. This scalability makes network expansion and upgrade more convenient. There is no need to replace the entire optical cable system, only the optical module needs to be replaced.
High-speed transmission and low latency:
SFP optical cable has the following advantages in high-speed data transmission and low latency requirements:
-
High-speed transmission: SFP optical cable can support a variety of transmission rates, including 10Gbps, 40Gbps and 100Gbps, etc. This makes SFP optical cable suitable for applications with high bandwidth requirements, such as server interconnects and storage network connections in data centers. High-speed transmission can provide faster data transmission speed, improve network performance and response time.
-
Low latency: The optical signal transmission speed of SFP optical cable is very fast, and the characteristics of light speed transmission give it the advantage of low latency. Low latency is very important for applications that have strict requirements on network performance, such as financial transactions and high-frequency trading, which require real-time data transmission and fast response times.
Factors to consider:
When selecting and using SFP optical cables, you also need to consider the following factors:
-
Fiber type and length: Select the appropriate fiber type (SMF or MMF) and length according to actual needs. For example, if long-distance transmission is required, SMF fiber that supports longer transmission distances should be selected.
-
Compatibility and vendor selection: Make sure to choose SFP optical cables that are compatible with your equipment and optical modules. At the same time, choose reliable suppliers and manufacturers to ensure product quality and technical support.
-
Environmental conditions: Consider the special requirements of the deployment environment, such as temperature, humidity, and vibration. Some SFP fiber optic cables may have better adaptability and durability for harsh environmental conditions.
How to install and maintain SFP cables
Connector type:
SFP optical cables usually use connector types such as LC (Lucent Connector) and SC (Subscriber Connector). These connector types have different features and uses:
-
LC connector: The LC connector is a miniaturized connector commonly used for high-density fiber optic connections. LC connectors have lower insertion loss and better reliability, and are suitable for scenarios that require high-density optical cable connections, such as data centers and enterprise networks.
-
SC connector: SC connector is a common connector type, which has a convenient plug-in design and high reliability. SC connectors are usually used for single-mode optical fiber connections and are widely used in enterprise networks and optical communications.
Install and maintain fiber optic cleaning and protection:
To ensure good optical signal transmission and equipment performance of SFP optical cables, it is very important to clean and protect the optical fibers. Here are some methods and precautions for fiber optic cleaning and protection:
-
Fiber Optic Cleaning: Regular cleaning of fiber optic connectors is key to maintaining good optical signal transmission. Using a lint-free cleaning cloth and an appropriate cleaning solution, gently wipe the connector end faces to remove dust, grease, and other contaminants. Be careful not to touch or damage the end face of the connector to avoid introducing new contamination.
-
Connector Protection: It is critical to protect connector end faces from contamination and damage. When the connector is not in use, use an appropriate dust cover or protective cap to protect the end faces. When plugging and unplugging connectors, pay attention to proper alignment and gentle insertion to avoid excessive bending or stretching of the fiber.
-
Environmental protection: Avoid exposing optical fiber to harsh environmental conditions, such as high temperature, humidity and strong vibration. When installing fiber optics, choose appropriate protection measures, such as fiber optic conduits, sheaths, and protective sleeves, to protect the fiber from external damage.
-
Regular inspection and maintenance: Regularly check the status and performance of fiber optic cable connections to ensure that the connector end faces are clean and have good connections. If connection problems or damage are found, take prompt repair measures, such as replacing the connector or cleaning the end face.
Compatibility and standards of SFP cables
MSA standards:
The multi-vendor compatibility of SFP optical cables is based on the MSA (Multi-Source Agreement) standard. MSA is an industry standard designed to ensure interoperability between optical modules and cables produced by different vendors. By following the MSA standard, SFP optical modules and cables from different vendors can be used interchangeably in the same SFP slot without additional compatibility issues.
The MSA standard defines specifications for optical modules in terms of physical dimensions, electrical interfaces, optical characteristics, and optional features. This enables consistent specifications and compatibility for optical modules from different vendors to ensure they can work properly in a variety of network equipment.
Electrical and optical specifications:
The electrical and optical specifications for SFP fiber optic cables are defined according to MSA standards. Here are some common electrical and optical specifications:
-
Transmit Power: The transmit power of SFP optical cable refers to the power level of the optical signal sent by the optical module. Transmit power is usually expressed in milliwatts (mW) or decibel milliwatts (dBm), and different types of SFP optical modules may have different transmit power ranges.
-
Receiver Sensitivity: The receiving sensitivity of SFP optical cable refers to the sensitivity level of the optical module in receiving optical signals. Receiving sensitivity is usually expressed in milliwatts (mW) or decibel milliwatts (dBm). Higher receiving sensitivity means that the optical module can receive weaker optical signals.
-
Operating temperature range: The operating temperature range of SFP optical cable refers to the temperature range in which the optical module can work normally. Different types of SFP optical modules have different operating temperature ranges, such as commercial, industrial or extended temperature.
In addition to the above specifications, the MSA standard also defines some other important specifications, such as fiber type, transmission rate, transmission distance, fiber interface type, etc. These specifications ensure interoperability and compatibility between SFP optical modules and optical cables produced by different vendors.
Summarize:
SFP optical cable is a high-performance optical fiber cable that uses a hot-swappable SFP interface to provide you with flexible and reliable optical fiber connection solutions. It supports a variety of fiber types and transmission rates, and is suitable for scenarios such as data centers, remote offices, and campus networks. By choosing SFP optical cable, you will enjoy the advantages of flexibility, scalability, high-speed transmission and low latency to meet your strict requirements for network performance.
- Can SFP connect to RJ45?
- Do I need SFP cable?
- What is the difference between SFP and DAC?
- What is the difference between SFP+ and DAC cable?
- Will SFP+ DAC work in SFP?
- Why is DAC cable used?
- Are DAC cables fiber?
- Is SFP active or passive?
- What is the difference between SFP+ and SFP cable?
- What is the difference between active and passive SFP cable?
-
100G QSFP28 to 2x50G QSFP28 active branch cable
-
100G QSFP28 to 2x50G QSFP28 active branch optical cable
-
100G QSFP28 to 2x50G QSFP28 passive branch cable
-
100G QSFP28 to 4-duplex LC active branch optical cable
-
100G QSFP28 to 4x25G SFP28 active branch cable
-
100G QSFP28 to 4x25G SFP28 active branch optical cable
-
100G QSFP28 to 4x25G SFP28 passive branch cable
-
10g sfp+ active optical cable
-
10g sfp+ direct attach cable