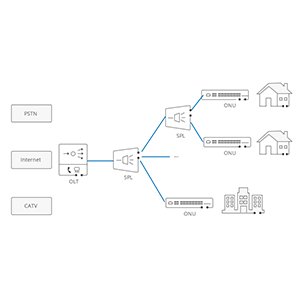
Hello everyone! I believe you must have some understanding of the application value of fiber optic branch cables in fiber optic networks. As a flexible and efficient optical fiber connection solution, optical fiber branch cables play an important role in data centers, building wiring and other fields. Today I am very happy to provide you with an in-depth analysis of the technical characteristics, main types and correct installation and management methods of fiber optic branch cables. By fully understanding the advantages of fiber optic branch cables, I believe you will be able to choose the best solution for your fiber optic network and further improve the overall cabling flexibility and operation and maintenance efficiency.
Overview of fiber optic branch cables
Let me give you an overview of fiber optic branch cables:
What is fiber optic branch cable
- Fiber optic branch cable is a composite optical cable with one trunk optical fiber and several branch optical fibers.
- Backbone fiber is used for long-distance transmission, while branch fiber is connected to end-user equipment.
- Branch cables can “branch” multiple branch lines from the trunk optical fiber to provide users with optical fiber access.
- It plays important distribution and access functions in fiber optic network layout.
Advantages of fiber optic branch cables compared to traditional fiber optic cables:
- Reduce the amount of wiring work required for optical fiber terminals: branch cables can be introduced into multiple terminals at one time.
- Improving the deployment flexibility of optical fiber networks: branch cable wiring is more convenient and flexible.
- Reduce the construction cost of the overall optical fiber network: branch cables can improve resource utilization efficiency.
- Facilitates subsequent expansion and maintenance of the optical fiber network: the branch structure is easy to manage and maintain.
Overview of the development history of optical fiber branch cables:
- The earliest optical fiber branch cables used mechanical docking to achieve branches.
- Subsequently, branch technology using fiber optic couplers to achieve fusion-free splicing emerged.
- Today, optical fiber branch cables are widely used in the construction of various optical fiber access networks.
- Plays an important distribution and access role in optical networks such as FTTH and FTTx.
In general, fiber optic branch cables play an indispensable role in the construction of fiber optic networks due to their advantages in reducing wiring projects and improving deployment flexibility. With the continuous advancement of technology, branch cables are increasingly used in the industry.
Technical characteristics of optical fiber branch cables
Let me introduce you to the technical characteristics of fiber optic branch cables in detail:
Physical structure and functional characteristics of optical fiber branch cables:
- Backbone optical fiber: used to provide long-distance transmission channels, usually using single-mode optical fiber.
- Branch optical fiber: branches from the trunk to provide user-end access services.
- Fiber optic coupler: realizes lossless coupling connection from trunk fiber to branch fiber.
- Protective tube: wraps and protects the trunk and branch optical fibers to prevent damage from external forces.
- Connector: Optical fiber connector used at the end of branch cable, such as SC, LC, etc.
Performance of optical fiber branch cables in terms of optics, mechanics, integration, etc.:
- Optical performance: The optical coupling loss of the branch interface is low, ensuring signal transmission quality. Optical fiber splicing losses are also effectively controlled.
- Mechanical properties: Excellent structural design, with good tensile and bending resistance. The outer sheath material has strong weather resistance and is suitable for deployment in outdoor environments.
- Integration: Compact structural design, capable of highly integrating trunk and branch optical fibers. Improved wiring efficiency and reduced overall space occupied.
Key technical indicators of optical fiber branch cables and their practical significance:
- Number of branches: determines the number of users that a single trunk can support at the same time.
- Branch fiber length: determines the maximum laying distance of user equipment.
- Optical coupling loss: determines the branch signal strength and affects the transmission quality.
- Mechanical strength index: determines the reliability and service life of branch cables.
- Outline size: determines the space utilization efficiency and wiring flexibility of branch cables.
In general, fiber optic branch cables play an irreplaceable role in the construction of fiber optic networks due to their excellent optical performance, mechanical properties and high degree of integration. The optimization of these technical indicators is the key to achieving efficient and reliable optical fiber network layout.
Main types of fiber optic branch cables
Let me introduce to you the main types of fiber optic branch cables, as well as their characteristics and application value in different application scenarios:
Common types of fiber optic breakout cables:
- Single-core branch cable: only one trunk optical fiber and several branch optical fibers.
- Multi-core branch cable: There are 2 or more trunk fibers, and corresponding branches.
- Pre-terminated branch cables: The trunk and branch fibers have been pre-terminated with connectors.
- On-site splittable branch cables: The main trunk and branches can be split on-site according to needs.
Differences in applicable scenarios of various types of fiber optic branch cables:
- Single-core branch cable: suitable for small-scale user access, and the wiring requirements are relatively simple. Branches are usually connected by direct welding or mechanical docking.
- Multi-core branch cable: It is suitable for large-scale user access and can introduce more branches at one time. Branches usually use fiber optic connectors to achieve fast splice-free connections.
- Pre-terminated branch cables: Connect the connectors in advance and quickly complete branch connections on site. Suitable for scenarios that require rapid deployment, such as FTTH, FTTx, etc.
- On-site splittable branch cables: The trunk and branch optical fibers can be flexibly split according to actual needs. Suitable for scenarios where wiring scheme changes are frequent.
Characteristics of different optical fiber branch cables in optical fiber networks:
- Improve the efficiency of fiber optic network deployment and shorten the construction cycle.
- Enhance the flexibility of optical fiber networks to meet changes in user access needs.
- Optimize the utilization of optical fiber resources and reduce network construction and maintenance costs.
- Provide important technical support for the smooth extension of optical fiber networks to user terminals.
In short, fiber optic branch cables present a variety of different types and connection forms according to different application scenarios. Various branch cables play an important role in improving the deployment efficiency of optical fiber networks and enhancing network flexibility. They are one of the key technologies for realizing high-quality optical fiber network construction.
Installation and management of fiber optic branch cables
Let me introduce to you the installation and management of fiber optic branch cables:
Correct installation process and precautions for fiber optic branch cables:
- Carefully plan the routing path of branch cables to ensure that the cables are routed reasonably and safely.
- Connect the main cable and branch cable connector ends correctly to ensure a stable and reliable connection.
- If it is a pre-terminated branch cable, just plug in the pre-terminated connector directly.
- If the branch cable is detachable on site, the branches need to be separated according to needs.
- Pay attention to protecting the optical fiber connector to avoid damage or contamination from external forces.
- Reserve adequate optical fiber surflus length for subsequent maintenance or capacity expansion.
Daily inspection, maintenance and management methods of optical fiber branch cables:
- Regularly visually check whether the outer sheath of the cable is damaged and whether the connector connection is firm.
- Use an optical power meter to test the optical power of each branch port to ensure normal transmission.
- Pay attention to keeping cables neatly routed and branch connectors clean to avoid accumulation of contamination.
- Clean the environment around the cable promptly to prevent debris from causing mechanical damage to the cable.
- For branch cables used for a long time, the aging degree needs to be checked regularly and replaced if necessary.
Common faults of optical fiber branch cables and their troubleshooting measures:
- The optical power of some branch ports decreases: Check whether the corresponding branch connector is damaged or contaminated and needs to be cleaned or replaced. Check whether the trunk optical fiber has increased loss caused by macro bending or damage.
- Mechanical damage to branch cables: Check whether the outer sheath of the cable is damaged and repair the damaged parts. If the damage is severe, the entire branch cable may need to be replaced.
- The connection of the branch connector is unstable: carefully check whether the connector is plugged in and out properly to ensure that the connection is firm and reliable. If the connector itself is damaged, it needs to be replaced with a new fiber optic connector.
In general, the correct installation and regular maintenance of fiber optic branch cables is crucial to ensuring the stable operation of the entire fiber optic network. Mastering the installation process, maintenance measures, and timely detection and elimination of faults are the keys to long-term reliable operation of branch cables.
Application of optical fiber branch cables in optical fiber networks
Let me introduce to you the typical applications of fiber optic branch cables in different fiber optic network application scenarios and its important role in improving network flexibility:
Application of optical fiber branch cables in data center networks:
- Data centers often require a large number of optical fiber terminals for interconnection.
- Multi-core branch cables can introduce multiple branches at one time to improve deployment efficiency.
- Pre-terminated breakout cables enable fast fiber optic interconnect connections.
Application of fiber optic branch cables in building fiber optic cabling:
- Building networks usually need to introduce branches from the backbone to each client.
- Single-core or multi-core branch cables can flexibly meet different user access needs.
- The compact structure of branch cables helps optimize fiber optic cabling space within the building.
Application of optical fiber branch cables in FTTH fiber-to-the-home network:
- The FTTH network needs to introduce branches from the trunk line to each home terminal.
- Pre-terminated branch cables can greatly simplify the construction process of user access.
- On-site detachable branch cables are helpful to meet changes in user needs.
The important role of optical fiber branch cables in improving network flexibility:
- Branch cables can be flexibly introduced according to user needs to improve deployment efficiency.
- The branch cable structure design is flexible and easy for subsequent expansion and maintenance of the network.
- Branch cables are beneficial to optimizing the utilization of optical fiber resources and reducing network construction costs.
- Branch cables are one of the key technologies to achieve highly flexible fiber optic network layout.
In general, fiber optic branch cables are widely used in various fiber optic network scenarios such as data centers, building fiber optics, and FTTH due to their advantages in simplifying construction, improving deployment efficiency, and optimizing resource utilization. It plays an irreplaceable and important role in improving the overall flexibility and scalability of optical fiber networks.
Summary
Fiber optic branch cables are undoubtedly the best choice in fiber optic network construction. Its excellent performance characteristics, flexible applicable scenarios, and key role in improving network cabling efficiency all highlight the important status of optical fiber branch cables. Whether in the field of data centers, building cabling or FTTH, fiber optic branch cables can inject powerful power into your fiber optic network to ensure efficient and orderly fiber optic connections.
We provide professional fiber optic cable products and installation management services, and are equipped with an experienced technical team to provide you with considerate guidance at any time. If you have any questions about selecting or using fiber optic branch cables, please feel free to contact us for communication.
Fiber Breakout Cable FAQ
A fiber breakout cable, also known as a breakout cable or fan-out cable, is a type of fiber optic cable that consists of multiple individual optical fibers bundled together and then broken out or separated into individual terminations.
The primary purpose of a fiber breakout cable is to provide a transition from a high-density, multi-fiber cable to individual, easily manageable, and terminated fiber optic cables. This facilitates connections and simplifies installation.
Fiber breakout cables typically have a central, multi-fiber cable core that is surrounded by a protective outer jacket. The individual fibers are then broken out and protected with their own small diameter jackets or tubes.
Fiber breakout cables are widely used in data centers, telecommunications networks, and other fiber optic installations where the transition from high-density to individual fiber connections is required, such as at patch panels or equipment interfaces.
Key advantages include improved cable management, easier termination and installation, and the ability to service or replace individual fibers without affecting the entire cable.
Fiber breakout cables are available in a wide range of fiber counts, typically ranging from 2 to 24 or more individual fibers, depending on the specific application and installation requirements.
The individual fibers in a breakout cable are typically terminated with various connector types, such as LC, SC, or ST, to facilitate easy connection to network equipment or patch panels.
Factors like the outer jacket material, fiber type (single-mode or multimode), and bend radius specifications are important to ensure the cable’s durability and performance in different environments.
Best practices include ensuring proper cable routing, strain relief, and organization to maintain the integrity of the individual fibers and the overall cable assembly.
Working with fiber breakout cables may require specialized tools, such as fiber optic strippers and cleave tools, as well as careful handling techniques to avoid damage to the individual fibers.
Fiber Breakout Cable Related Products
-
800G OSFP to 2x400G OSFP passive branch cable
-
40G QSFP+ to 4x10G SFP+ passive branch cable
-
400G QSFP-DD to 8x50G SFP56 passive branch cable
-
400G QSFP-DD to 4x100G QSFP56 passive branch cable
-
400G QSFP-DD to 2x200G QSFP56 passive branch cable
-
200G QSFP56 to 4x50G SFP56 passive branch cable
-
200G QSFP56 to 2x100G QSFP56 passive branch cable
-
200G QSFP-DD to 8x25G SFP28 passive branch cable
-
200G QSFP-DD to 4x50G QSFP28 passive branch cable