In this article, I will delve into the role and advantages of OLT (Optical Line Terminal) in next-generation fiber optic networks. We will introduce the definition and functions of OLT in optical fiber networks and its key advantages in building high-speed, stable and scalable networks. By understanding the different types of OLTs and their standards, you will be able to choose the best solution for your network needs. Let us explore the outstanding performance of OLT in the next generation optical fiber network!
What is OLT
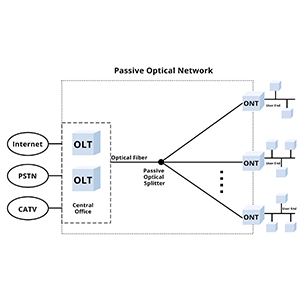
OLT (Optical Line Terminal) is a key device in the optical fiber network, used for optical fiber switching and transmission between optical fibers and users in the optical fiber access network (FTTx). It is an important node in the optical fiber communication network, responsible for converting optical signals into electrical signals and communicating with user equipment.
Basic definition and functions of OLT:
OLT is a central node device located in the optical fiber network. It has the following basic definitions and functions:
- Optical fiber access: As the starting point of the optical fiber network, OLT receives optical fiber signals and processes and forwards them.
- Optical signal conversion: OLT converts optical signals into electrical signals for further processing and transmission in the telecommunications network.
- Optical fiber switching: OLT performs switching between optical fibers in the optical fiber network, forwards data from the sending port to the receiving port, and ensures reliable transmission of data.
- Management and control: OLT is responsible for managing and controlling various nodes and user equipment in the optical fiber network, including configuration, monitoring and troubleshooting.
The components and working principle of OLT:
OLT usually consists of the following components:
- PON port: used to connect to optical fiber transmission systems to receive and send optical signals.
- Optical receivers and transmitters: used to receive and transmit optical signals.
- Optical Network Unit (ONU) interface: used to connect user equipment, such as optical modems or fiber optic modems.
- Switching matrix: used to implement switching and forwarding between optical fibers.
- Control and management module: Responsible for configuring, monitoring and managing OLT equipment and optical fiber networks.
The working principle of OLT is as follows:
- Receive optical signals: OLT receives optical signals through the PON port, which comes from the data sent by the user equipment through the optical fiber transmission system.
- Optical signal conversion: OLT uses optical receivers to convert optical signals into electrical signals for processing and transmission in the telecommunications network.
- Fiber switching: OLT forwards the received data to the ONU interface of the target user equipment to realize switching between fibers.
- Management and control: OLT configures, monitors and manages the optical fiber network through the control and management module to ensure the normal operation and troubleshooting of the network.
Overview of different types of OLTs and their standards:
OLT can be classified according to its working mode and standards. The following are several common OLT types and related standards:
- EPON (Ethernet Passive Optical Network): Based on Ethernet technology, it adopts passive optical fiber network structure and complies with IEEE 802.3ah standard.
- GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network): uses wavelength division multiplexing technology to provide higher bandwidth and longer transmission distance, and complies with the ITU-T G.984 standard.
- XG-PON (10G Passive Optical Network): Provides a 10Gbps rate, supports symmetric and asymmetric transmission, and complies with the ITU-T G.987 standard.
- XGS-PON (10G Symmetric Passive Optical Network): Provides symmetrical 10Gbps transmission rate and complies with ITU-T G.9807 standard.
These different types of OLT provide different bandwidths, transmission rates and functions based on the standards and technologies they support to meet the needs of various optical fiber networks.
Key features and advantages of OLT
OLT has many key features and advantages that make it play an important role in fiber optic networks:
-
High bandwidth: OLT supports high-bandwidth transmission and can meet the needs of large amounts of data and high-speed transmission in modern networks. It can provide enough bandwidth to support high-definition video, large-capacity file transfer and real-time applications.
-
Distributed architecture: OLT adopts a distributed architecture to distribute the core functions of the optical fiber network to different nodes. This architecture allows flexible deployment and management, improving network reliability and scalability.
-
Flexibility: OLT has flexible configuration and management functions that can be customized and adjusted according to needs. It can adapt to different network topologies and business needs, and supports flexible bandwidth allocation and service quality control.
-
High-speed data transmission: OLT supports high-speed data transmission and can provide Gigabit or even ten Gbps level transmission rates. This allows users to quickly access and transfer large files, enabling efficient data communication.
-
Long-distance coverage: OLT can achieve long-distance coverage through optical fiber transmission, overcoming the distance limitations of traditional copper cable networks. It can extend high-speed data transmission to a range of tens or even hundreds of kilometers.
-
Multi-service support: OLT supports multiple services, including Internet access, IP telephony, IPTV, etc. It can handle different types of traffic and services at the same time, providing users with diverse communication and entertainment experiences.
The importance of OLT in achieving high-speed, stable and scalable networks:
OLT plays a key role in optical fiber networks and is crucial to achieving high-speed, stable and scalable networks.
-
High-speed network: OLT provides high-speed data transmission capabilities, meeting the needs of modern networks for high bandwidth and fast data transmission. It allows users to access the Internet at faster speeds, transfer large files, and enjoy applications such as high-definition videos.
-
Stability and reliability: OLT provides stable and reliable connections through optical fiber transmission. Optical fiber networks have strong anti-interference capabilities against electromagnetic interference and signal attenuation, and can provide more stable network connections and lower data loss rates.
-
Scalability: The distributed architecture and flexibility of OLT allow the optical network to be easily expanded and upgraded. By adding OLT nodes and optical fiber links, the coverage and capacity of the network can be easily expanded to meet growing user needs.
To sum up, the key features and advantages of OLT include high bandwidth, distributed architecture, flexibility, high-speed data transmission, long-distance coverage and multi-service support. It plays an important role in achieving high-speed, stable and scalable networks, providing users with advanced communications and Internet experiences.
The role and function of OLT in optical fiber network
OLT plays a key role in the fiber access network (Fiber Access Network) and has multiple important functions to achieve efficient data transmission and connection management.
Key roles:
- Optical fiber access starting point: OLT is the starting point of the optical fiber network. It receives optical signals from user equipment and processes and forwards them.
- Central node: As the central node of the optical fiber network, OLT connects the optical fiber transmission system and user equipment, and is responsible for the conversion of optical signals and the exchange of data.
- Management node: OLT is responsible for managing and controlling various nodes and user equipment in the optical fiber network, including configuration, monitoring and troubleshooting.
Main functions:
- Optical signal conversion: OLT converts optical signals into electrical signals for further processing and transmission in the telecommunications network. It uses an optical receiver to convert optical signals into electrical signals and an optical transmitter to convert electrical signals into optical signals.
- Multiplexing: OLT uses multiplexing technology to combine the data streams of multiple users into an optical signal and transmit it to the optical fiber network. This technology allows multiple users to share the same fiber and efficiently utilize bandwidth resources.
- Data distribution: OLT distributes the received data to the ONU interface of the target user equipment to realize exchange and data transmission between optical fibers.
Application scenarios and uses:
- Home broadband access: OLT plays a key role in home broadband networks, connecting optical fiber transmission systems and home user equipment to provide high-speed and stable Internet access services.
- Enterprise network: OLT is widely used in enterprise networks to connect the enterprise’s internal network and the external Internet, provide high-speed data transmission and stable connections, and meet the communication and data needs of enterprises.
- Public services: OLT is used to provide public services, such as urban broadband networks, school and hospital networks, etc. It can support a large number of users to access high-speed Internet at the same time and provide high-quality services and application experience.
In short, OLT plays a key role in optical fiber networks, with major functions such as optical signal conversion, multiplexing, and data distribution. It is widely used in home broadband, enterprise networks and public services, providing users with high-speed, stable and reliable data connections and communication services.
Comparison between OLT and other network equipment
OLT (Optical Line Terminal), ONU (Optical Network Unit) and ONT (Optical Network Terminal) are common devices in optical fiber networks, each with different functions and roles.
OLT (Optical Terminal Equipment):
- Role: OLT is the central node of the optical fiber access network and is responsible for managing and controlling various nodes and user equipment in the optical fiber network.
- Function: OLT has the functions of optical signal conversion, multiplexing and data distribution. It converts optical signals into electrical signals to realize data exchange and transmission.
ONU (Optical Network Unit):
- Role: ONU is a terminal node in the optical fiber access network. It is usually installed at the user’s location and is used to connect user equipment and the optical fiber network.
- Function: ONU is responsible for receiving the optical signal from the OLT and converting it into an electrical signal, and then transmits the data to the user equipment. It also has functions such as data parsing, interface conversion and user authentication.
ONT (Optical Network Terminal):
- Role: ONT is a special type of ONU, usually used for terminal equipment in home or enterprise networks.
- Function: ONT has functions similar to ONU, including optical signal conversion and data transmission. It also integrates routers, switches and other network functions to provide users with more comprehensive network connections and services.
The reasons why OLT plays a unique role and function in optical fiber networks:
OLT plays a unique role and function in the optical fiber network, which is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
-
Central node: As the central node of the optical fiber network, OLT has centralized management and control capabilities. It can manage and monitor the entire network, configure and troubleshoot user devices, and provide a unified management interface and control functions.
-
High bandwidth and multiplexing: OLT has high bandwidth transmission capabilities and multiplexing technology, and can support data transmission for multiple users at the same time. It can combine the data streams of multiple users into one optical signal and efficiently utilize the bandwidth resources of optical fiber.
-
Flexibility and scalability: OLT has flexible configuration and expansion capabilities and can be customized and adjusted according to network needs. It supports different types of optical fiber interfaces, network topologies and business needs, and can easily expand and upgrade network capacity and coverage.
-
Network management and control: As the management node of the optical fiber network, OLT has powerful network management and control functions. It can monitor network performance and quality, implement bandwidth allocation and service quality control, and provide security authentication and access control functions.
To sum up, OLT plays a unique role and function in the optical fiber network through its central node management and control capabilities, high-bandwidth transmission and multiplexing technology, flexibility and scalability, and Powerful network management and control functions provide efficient, stable and reliable data transmission and connection management for optical fiber networks.
OLT selection and deployment
- Key factors and considerations for selecting and purchasing OLT:
-
Compatibility: Ensure the selected OLT is compatible with existing fiber optic network equipment and standards for seamless integrationSuccess and upgrade.
-
Performance and capacity: Choose an OLT with sufficient performance and capacity based on network requirements and expected user scale. Considering bandwidth needs and user growth, choose equipment that supports high-speed data transfer and multi-user connections.
-
Scalability: Ensure that the selected OLT has good scalability so that network capacity and coverage can be easily expanded when needed.
-
Management and control functions: Evaluate the management and control functions of the selected OLT, including configuration interface, troubleshooting tools, performance monitoring and remote management.
-
Reliability and stability: Choose suppliers and brands that are reliable and have good reputations, and ensure that the selected OLT has high reliability and stability to ensure the continuous operation of the network and service quality.
-
Cost-effectiveness: Comprehensive consideration of factors such as equipment price, maintenance costs, and performance, select an OLT with good cost performance.
- OLT deployment strategies and best practices:
-
Network planning: Carry out adequate network planning and design before deploying OLT. Determine the network topology, the location and connection method of the OLT, and consider factors such as bandwidth requirements, user distribution, and service area.
-
Redundancy and backup: To ensure high availability and fault tolerance of the network, consider using redundant OLT equipment and backup optical fiber connections. This can reduce the impact of single points of failure and improve network stability.
-
Security protection: Take necessary security measures, such as access control, identity authentication, and data encryption, to protect data and communication security in the OLT and network.
-
Performance optimization: Carry out appropriate configuration and optimization to ensure that the OLT’s performance and bandwidth allocation meet network needs. Optimize parameters such as data traffic management, service quality control, and cache settings.
-
Regular maintenance and upgrades: Perform regular OLT maintenance work, including firmware upgrades, performance monitoring, and troubleshooting. Timely updates and fixes software vulnerabilities to ensure network security and performance.
- FAQs and troubleshooting suggestions:
-
Connection problems: If there are connection problems, first check whether the fiber optic connection is plugged in correctly and make sure the connection is stable. Problems can also be identified by checking the status of optical modules and fiber interfaces.
-
Troubleshooting tools: Utilize the troubleshooting tools and logging provided by the OLT to determine the root cause of the problem. Check logs, event records, and performance statistics to help diagnose and resolve problems.
-
Bandwidth issues: If users experience bandwidth issues, they can check that bandwidth allocation and quality of service settings are correct. Optimize bandwidth management and traffic control to improve user bandwidth experience.
-
Software updates and upgrades: Check the OLT regularly for software updates and firmware upgrades for new features and security fixes. Make sure devices are running the latest version of software to reduce potential glitches and vulnerabilities.
-
Manufacturer support: If you encounter complex problems or unresolved faults, contact the OLT supplier’s technical support team in a timely manner. They can provide professional guidance and support to help you resolve issues and restore normal operation of your network.
Please note that OLT deployment and troubleshooting may vary by vendor and specific circumstances. During the actual deployment and maintenance process, it is recommended to refer to the specific documentation, guidelines and best practices provided by the vendor to ensure the correct and effective use of OLT equipment.
Overview:
Thank you for reading our blog! Through the in-depth discussion of this article, you will have a more comprehensive understanding of the role and advantages of OLT (Optical Line Terminal) in the next generation optical fiber network. As a key device in the optical fiber network, OLT plays an important role in the optical fiber access network (Fiber Access Network). OLT has key features such as high bandwidth, distributed architecture and flexibility, bringing the advantages of high-speed data transmission, long-distance coverage and multi-service support to optical fiber networks.
OLT plays an important role in application scenarios such as home broadband, enterprise networks, and public services. We provide high-quality OLT products to meet your needs for building next-generation optical fiber networks. By choosing our products, you can get reliable, high-speed and scalable network connections to meet the requirements of different application needs. If you have any needs or questions about OLT, our team is here to help.
Optical Line Terminal FAQ
The OLT serves as the central point of aggregation and control in a PON. It receives data from multiple Optical Network Units (ONUs) and forwards it to the appropriate destination within the network.
The primary functions of an OLT include converting electrical signals into optical signals for transmission over fiber, managing the upstream and downstream data traffic in a PON, and providing control and management of the optical network.
An OLT typically consists of a line card, switching fabric, management module, power supply, and uplink interfaces. These components work together to enable connectivity, traffic management, and network control.
An OLT is the provider-side equipment located in the central office or data center, responsible for aggregating and distributing data over the PON. An Optical Network Terminal (ONT) or Optical Network Unit (ONU) is the customer-side equipment located at the subscriber’s premises, used to receive and transmit data over the PON.
An OLT communicates with ONUs using the Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) or Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) protocol. It allocates time slots or wavelengths for upstream and downstream transmission, allowing data exchange between the OLT and ONUs.
The maximum number of ONUs supported by an OLT depends on various factors, including the OLT model, PON standard (GPON, EPON, etc.), and system capacity. OLTs can typically support multiple ONUs, ranging from a few dozen to several thousand.
Yes, an OLT can support multiple PONs simultaneously. It can manage and provide services for different PON technologies or multiple PONs within the same network infrastructure.
Using an OLT in a PON architecture offers benefits such as efficient bandwidth utilization, centralized management and control, scalability for adding new subscribers, and the ability to deliver various services over a single fiber infrastructure.
Choosing the right OLT involves considering factors such as the desired PON technology, system capacity, scalability requirements, supported features, and compatibility with other network components. Consulting with network professionals or vendors can help determine the most suitable OLT for your network needs.