Fiber optic cables undoubtedly play an important role in high-speed communication networks. This article will focus on the characteristics of ribbon fiber optic cables. We will first outline the basic components of fiber optic cables and compare different types of fiber optic cables, such as single-fiber and multi-fiber. Next, we will define the physical structure and manufacturing process of ribbon fiber optic cables and explain their advantages in terms of density, flexibility, etc.
We will analyze the application requirements of ribbon fiber optic cables in different network environments, such as data centers, telecommunications trunk networks, FTTH and other scenarios. In addition, we will introduce the main technical parameters of ribbon fiber optic cables, such as the number of fibers, loss, etc., and explain the basis for selecting suitable ribbon fiber optic cables in different applications. Finally, we will explain the installation and wiring points of ribbon fiber optic cables and provide specific suggestions for regular inspection and maintenance.
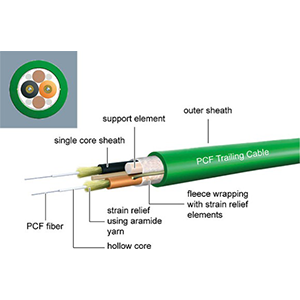
Basic structure and classification of optical fiber cable
I will introduce the basic structure and various main types of optical fiber cable in more detail:
Basic structure of optical fiber cable:
- Optical fiber core (Core): Made of high-purity quartz glass or plastic, with a diameter of generally 8-50 microns, used to carry the transmission of optical signals.
- Optical fiber cladding (Cladding): Located on the periphery of the optical fiber core, made of low-refractive index glass or plastic of the same material, with a thickness of about 125 microns. It plays the role of an optical waveguide, allowing the optical signal to be reflected and propagated inside the optical fiber core.
- Buffer (Buffer): Wrapped outside the optical fiber cladding, usually made of plastic material, with a thickness of about 0.25-0.9 mm. Used to isolate the external environment and protect the optical fiber core and cladding from mechanical damage, moisture, chemical corrosion, etc.
- Strengthening Layer: Located outside the buffer layer, it is woven from steel wire, aramid fiber or glass fiber. It provides mechanical strength to prevent external forces from damaging the optical fiber.
- Jacket: The outermost protective layer, usually made of polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride and other materials, with a thickness of about 0.5-3 mm. It is used to prevent the optical fiber cable from being stretched, squeezed, cut, corroded and other external damage.
Main categories of optical fiber cables:
- Single-Mode Fiber Cable: The optical fiber core has a small diameter and only supports one transmission mode. It is suitable for long-distance, high-speed transmission, such as trunk networks.
- Multi-Mode Fiber Cable: The optical fiber core has a large diameter and can support multiple transmission modes. It is suitable for short-distance, low-speed transmission, such as local area networks.
- Dual-core fiber optic cable: contains two independent optical fiber cores, which can realize two-way communication or backup transmission.
- Multi-core fiber optic cable: consists of multiple (usually 4, 8, 12 or 24) independent optical fiber cores, used for large-capacity and high-density transmission.
- Optical cable: formed by bundling multiple optical fiber cables (such as single-mode or multi-mode), suitable for large-capacity and long-distance optical fiber communication networks.
The above is an introduction to the basic structure and main classification of optical fiber cables. The appropriate type of optical fiber cable will be selected in different application scenarios to meet the requirements of transmission rate, distance, capacity, etc.
Features of Ribbon Fiber Cable
Let me introduce you to the features of ribbon fiber cable in detail:
Physical structure and manufacturing process of ribbon fiber cable:
- Ribbon fiber cable is composed of multiple small optical fibers arranged in parallel, presenting a flat ribbon appearance.
- Each optical fiber has an independent core, cladding and buffer layer, arranged side by side in a common outer sheath.
- During the manufacturing process, multiple pre-processed optical fibers are first arranged side by side and then uniformly coated in an outer sheath. This manufacturing process makes the ribbon cable highly consistent.
Advantages of ribbon fiber cable:
- High density: Because the optical fibers are arranged side by side, ribbon cables can accommodate more optical fibers under the same cross-sectional area. This enables it to transmit higher information capacity in a limited space.
- Flexibility: Compared with round fiber optic cables, ribbon cables have stronger bendability and flexibility. This feature makes it easier to install in narrow or curved spaces.
- Space saving: The flat structure makes ribbon fiber optic cables take up less space when wiring, which is conducive to cable management and wiring.
- Easy to identify: Due to the flat shape, ribbon cables are easier to identify and distinguish in complex cable environments.
- Good compatibility: Ribbon cables are well compatible with various standard interfaces and devices.
In short, ribbon fiber optic cables rely on their unique physical structure and manufacturing process, showing obvious advantages in density, flexibility, space utilization, etc., and are more advantageous in some specific application scenarios.
Main application scenarios of ribbon fiber optic cables
Let me introduce you to the main application scenarios of ribbon fiber optic cables in detail:
Data center applications:
- The wiring environment inside the data center is very complex, with narrow space and high density requirements.
- Ribbon fiber optic cables can be laid more efficiently in racks, ceilings and other spaces due to their flat and flexible characteristics.
- At the same time, high-density transmission capacity can also meet the needs of massive data processing and transmission in data centers.
Telecom trunk network applications:
- Telecom trunk networks require long-distance, high-capacity fiber optic transmission capabilities.
- Ribbon fiber optic cables can save pipeline space through a compact shape, while taking into account flexibility and easy deployment.
- In addition, the consistency of ribbon cables can also ensure the stable and reliable operation of the trunk network.
FTTH (Fiber to the Home) Applications:
- FTTH networks require that optical fibers can be flexibly inserted into various types of residences and buildings.
- The flexibility and small size of ribbon fiber cables enable them to better pass through narrow building spaces and meet the needs of home wiring.
- At the same time, its flat shape is also conducive to the neat placement and management of home cables.
Other Application Scenarios:
- Aerospace: Ribbon fiber cables are very suitable due to weight and wiring requirements.
- Automotive Electronics: Ribbon cables in vehicle networks can better adapt to the bending and deformation of the vehicle body.
- Industrial Automation: Ribbon cables are more convenient to lay in narrow and complex industrial equipment.
In general, the unique advantages of ribbon fiber cables can be fully utilized in different network environments, making it one of the widely used fiber optic transmission solutions.
Performance indicators and selection of ribbon fiber cables
Let me introduce you to the performance indicators of ribbon fiber cables and the selection considerations in different application scenarios in detail:
Main technical parameters of ribbon fiber cables:
- Number of optical fibers: Usually there are 4, 8, 12, 24 channels to meet different capacity requirements.
- Type of optical fiber: Single-mode or multi-mode optical fiber can be selected, depending on the transmission distance and rate requirements.
- Optical fiber loss: It is related to factors such as optical fiber material and length, and is generally less than 0.5dB/km.
- Mechanical strength: provided by the reinforcement layer, meeting certain tensile, compression and bending capabilities.
- Outer diameter size: usually between 3-5mm, flat design is conducive to wiring.
- Operating temperature range: -20℃~+70℃, can adapt to certain harsh environments.
Choice basis in different applications:
- Data center: 12 or 24 core single-mode optical fiber is preferred, taking into account high density and long distance requirements. Pay attention to loss and bending performance.
- Telecom trunk network: Single-mode optical fiber is the first choice, and 4-24 cores can be selected according to the transmission capacity. Pay attention to mechanical strength and tensile properties.
- FTTH application: Multimode optical fiber is more suitable, 4-8 cores can meet the needs of home access. More attention is paid to flexibility and size.
- Industrial automation: Mechanical strength and anti-interference performance are more critical, and 4-8 core multimode optical fiber is often used.
- Aerospace: Weight and size restrictions are strict, and 4-8 core single-mode optical fiber is an ideal choice.
In short, when choosing a suitable ribbon fiber cable, it is necessary to comprehensively consider multiple indicators such as the number of optical fibers, optical fiber type, transmission performance, and mechanical characteristics, and make targeted configurations according to the needs of specific application scenarios.
Installation and maintenance of ribbon fiber cables
Let me introduce you to the installation and maintenance of ribbon fiber cables in detail:
Main points for installation and wiring of ribbon fiber cables:
- Check whether the cable surface is damaged and ensure that the cable is intact before installation.
- Plan the cable routing path and try to avoid excessive bending or stretching.
- Use a dedicated fiber stripping tool to carefully strip the outer sheath to expose the inner fiber core.
- Terminate the stripped fiber to the optical connector, and clean and weld it carefully.
- Use appropriate fixing methods, such as cable ties, plastic card slots, etc., to prevent the cable from hanging in the air.
- For areas that need to be inserted into pipes or enter narrow spaces, a dedicated fiber introduction tool can be used.
- Organize the cable lines and clearly mark the corresponding relationship between the fiber ports.
Regular inspection and maintenance treatment suggestions:
- Perform a comprehensive inspection of the cable every quarter to check for mechanical damage, bending deformation, etc.
- Check whether the fiber connector is contaminated or damaged, and clean or re-weld it if necessary.
- Monitor the fiber transmission performance, such as power loss, etc., and promptly detect and handle abnormal conditions.
- Keep the cable routing neat and orderly to avoid being squeezed or pulled by other equipment or objects.
- For cables exposed to harsh environments, they should also be regularly checked for moisture or corrosion.
- For cables that have been used for a long time, partial replacement may be considered to improve reliability.
In summary, the correct installation and effective maintenance of ribbon fiber cables are essential to ensure their long-term stable operation. By following relevant operating procedures, its advantages can be maximized.
Summary
The correct selection and deployment of ribbon fiber cables is essential for high-performance and high-density network architectures. Our company has long focused on the research and development and production of optical communication equipment and its supporting products, and has rich industry experience. The various types of ribbon fiber cable products we provide have reached the industry-leading level in terms of transmission performance and reliability, and can meet your demanding needs for flexible and efficient network construction.
Whether you need to deploy ribbon fiber cables in telecom operator networks, data centers, or enterprise campuses, we can provide you with customized solutions. At the same time, our professional team will provide you with a full range of technical support, including on-site surveys, solution design, and equipment installation and maintenance. Contact us now to learn more about the application of ribbon fiber cables.
ribbon fiber optic cable FAQ
Ribbon fiber optic cable contains multiple (typically 2-12) individual optical fibers arranged in a flat, ribbon-like configuration.
Ribbon fiber features the fibers arranged in parallel, while standard cable has individual fibers twisted or bundled together.
Key benefits include higher fiber density, faster installation, and simplified splicing and termination compared to individual fiber cables.
Ribbon fiber is commonly used in backbone networks, cable TV infrastructure, and high-density data center applications.
Common fiber counts range from 2 fibers up to 12 fibers per ribbon, with 4, 8, and 12 being the most common.
Ribbon cables use specialized ribbon connectors and fusion splicers designed to handle the multi-fiber ribbon format.
Ribbon cables are typically wider but thinner than bundled fiber cables, with diameters ranging from 3-12mm.
Yes, ribbon fiber can be used interchangeably with standard fiber for most applications, with some specialized installation techniques.
Drawbacks include higher initial cost, more complex handling, and potential for higher signal loss compared to single-fiber cables.
Yes, organizations like the TIA and IEC have defined standards for ribbon fiber construction, performance, and testing.