In this article, I will delve into the role and advantages of SOHO (Small Office/Home Office) networks in small offices and home offices. We will introduce the definition and characteristics of a SOHO network and its importance in meeting the network needs of small offices and home offices. By understanding the key equipment, technologies and security measures of SOHO networks, you will be able to build a reliable, secure and efficient SOHO network. Let’s explore the wonderful applications of SOHO networks in small offices and home offices!
What is SOHO network
SOHO network refers to Small Office/Home Office (Small Office/Home Office) network, which is designed to meet the network needs of small-scale office environments or home office environments. The following is an introduction to the basic definition, characteristics, scale and scope of SOHO networks, as well as its common components and infrastructure:
SOHO network is a network system designed to meet the network needs of small offices or home offices. It has the following basic characteristics:
- Small scale: SOHO networks are generally suitable for small office or home office environments and cover a relatively small number of users.
- Affordable: SOHO network solutions are often available at affordable prices, suitable for small businesses or personal use.
- Simple and easy to use: SOHO network products and equipment usually have simple and easy-to-use interfaces and configurations, and do not require complex professional skills to set up and manage.
- Basic functions: SOHO networks usually provide basic network functions, such as Internet access, LAN connection, file sharing, and printer sharing.
The size and scope of a SOHO network can vary based on specific needs and size. Generally speaking, SOHO network includes the following aspects:
- Number of users: SOHO networks are generally suitable for a small number of users, such as personal use, home offices, or small teams.
- Scope: A SOHO network can cover a small office, home environment or remote work location, providing LAN connectivity and Internet access.
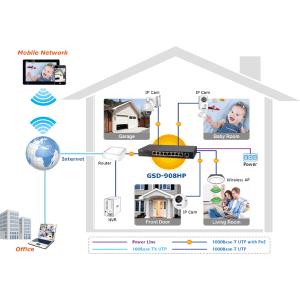
SOHO networks usually consist of the following components and infrastructure:
- Router: A core device used to provide Internet access and network connectivity, usually with firewall and Network Address Translation (NAT) capabilities.
- Switch: used to establish device connections and communications within a local area network (LAN) to achieve data exchange and sharing.
- Wireless Access Point (WAP): Provides wireless network connectivity, allowing users to connect to the network wirelessly.
- Server: used to store and share resources such as files and printers, and can also be used to provide specific network services, such as email, websites, etc.
- Terminal devices: including personal computers, laptops, smartphones, tablets, etc., used to access and use SOHO network resources.
- Firewall: Used to protect network security and prevent unauthorized access and network attacks.
- Data storage devices: such as network storage devices (NAS) or cloud storage services, used to back up and store important data.
- Cables and cables: Network cables and cables used to connect various devices, such as Ethernet cables, optical fibers, etc.
Please note that the specific configuration and equipment selection for a SOHO network may vary based on specific needs and budget. Based on actual needs and requirements, the SOHO network can be customized and expanded to meet the network needs of individuals or small offices.
Key equipment and technology
In SOHO networks, common key devices include routers, switches and wireless access points. The following is an introduction to the roles and functions of these devices in establishing and managing SOHO networks, as well as the key technologies used in SOHO networks, such as Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) and Virtual Private Network (VPN):
Key equipment:
Router:
- Role and function: The router is one of the most critical devices in the SOHO network, used to connect different networks and transmit data packets. It has routing capabilities that can transport packets from one network to another based on the network address. Additionally, the router provides Network Address Translation (NAT) functionality, allowing multiple devices to access the Internet through a single public IP address.
Switch:
- Role and function: Switches are used in SOHO networks to establish device connections and communications within the local area network (LAN). It plays the role of data exchange, can transmit data packets within the LAN, and deliver the data packets to the target device based on the MAC address. Switches can also provide network segmentation and virtual LAN (VLAN) capabilities for network isolation and security.
Wireless Access Point (WAP):
- Role and function: Wireless access points are used to provide wireless network connections in SOHO networks. It allows wireless devices such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets to connect to the network via Wi-Fi. Wireless access points provide network access over an area covered by a wireless signal and communicate with a wired network connection.
Key technologies:
Wireless LAN (WLAN):
- Role and function: WLAN technology allows devices to connect to local area networks and the Internet wirelessly. It uses wireless access points as access points to transmit data via wireless signals. WLAN technology provides flexibility and convenience, allowing users to move freely within the coverage area and enabling wireless devices to interconnect and share resources.
Virtual Private Network (VPN):
- Role and function: VPN technology is used to establish a secure remote access connection in the SOHO network. It uses encryption and tunneling technology to create a secure connection on a public network (such as the Internet) so that remote users can safely access LAN resources. VPN technology ensures data confidentiality and integrity and provides remote access security.
These key devices and technologies play an important role in the SOHO network, helping to realize connections between devices, data transmission and network access. They provide an efficient network infrastructure that enables users to network and share resources in a small office or home office environment. Depending on specific needs, other devices and technologies can also be used to extend and enhance the functionality of the SOHO network.
Cyber Security and Data Protection
Cybersecurity and data protection are crucial in SOHO networks. Although the SOHO network is smaller, it still faces cyber attacks, data leaks and other security threats. The following are the reasons to emphasize the importance of network security and data protection in SOHO networks, as well as some key measures and backup recovery strategies to protect SOHO networks:
Importance:
- Data protection: SOHO network may contain important business data, customer information and personal privacy data. Compromised, lost or tampered data can have serious consequences, including financial loss, reputational damage and legal liability.
- Network security: The SOHO network is connected to the Internet, so it is easy to become the target of network attacks. Unauthorized access, malware and other cyberattacks can lead to data breaches, service interruptions and system crashes.
Key measures:
- Firewall: Installing and configuring a firewall is an important step in protecting the SOHO network. Firewalls can monitor and control network traffic to prevent unauthorized access and malicious attacks. Ensure that firewall software and firmware are always updated and that appropriate rules and policies are configured.
- Encrypted communications: Use encryption protocols (such as TLS/SSL) to protect network communications, especially when transmitting sensitive data over the Internet. Encryption can ensure the confidentiality of data during transmission and prevent eavesdropping and tampering.
- Strong passwords and authentication: Set strong passwords for all network devices and accounts, and change them regularly. Enable multi-factor authentication (such as using passwords and verification codes) for added security.
- Security updates and patches: Regularly update operating systems, applications, and network devices with security patches and updates to fix known vulnerabilities and strengthen security.
- Security Awareness Training: Educate and train network users on common network threats and security best practices, such as identifying malicious emails and avoiding clicking on suspicious links.
Backup and recovery strategy:
- Regular backup: Develop a regular backup strategy to ensure regular backup of important data. Backup data should be stored in a secure location, which can be a local external hard drive, a network storage device (NAS), or a cloud storage service.
- Data recovery testing: Regularly test the reliability and recoverability of backup data. Ensure that the backup data can be restored smoothly and verify that the recovery process is effective.
- Offline backup: Store critical data backup on offline media, such as offline hard disk or tape. This prevents cyberattacks such as ransomware from harming your backup data.
By taking these network security and data protection measures, SOHO networks can better protect sensitive data, reduce security risks, and ensure continued business operations. It is important to regularly review and update security policies to adapt to the changing network environment and security threats.
Network extensions and remote access
Expanding SOHO networks to accommodate growth needs and enable remote access are important requirements in the modern work environment. The following is an introduction on how to expand the SOHO network and achieve remote access, as well as the application of cloud services and remote collaboration tools in the SOHO network:
Network extension:
- Add equipment: Add network equipment such as routers, switches, and wireless access points as needed to support more users and device connections. Ensure network equipment has sufficient performance and bandwidth to meet growth needs.
- Network segmentation and VLAN: Using network segmentation and virtual LAN (VLAN) technology to divide the network into logical subnets can achieve resource isolation, security and better network performance.
- Expand wireless coverage: Add wireless access points as needed to cover a larger area or provide better wireless signal strength. Use a wireless extender or bridge to extend your existing wireless network coverage.
Remote access:
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): By setting up a VPN server in the SOHO network, remote users can securely access LAN resources through the Internet. VPNs provide encrypted remote connections, allowing users to access files, applications, and other network resources in a secure manner.
- Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP): Using tools that support Remote Desktop Protocol, such as Windows Remote Desktop, you can remotely log in to a computer located in the SOHO network and operate the computer desktop during remote access.
- Cloud storage and file synchronization: Store important files and data in cloud service providers (such as Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive, etc.) so that files can be accessed and synchronized anywhere. This enables data access and sharing across devices and improves remote work efficiency.
Cloud services and remote collaboration tools:
- Cloud services: Using cloud services, such as cloud storage, cloud applications, and cloud infrastructure, data and applications can be hosted in the cloud, reducing dependence on local resources. Cloud services can provide scalability, elasticity and flexibility, allowing SOHO networks to adapt to changing needs.
- Remote collaboration tools: Use remote collaboration tools, such as video conferencing software (such as Zoom, Microsoft Teams), instant messaging tools (such as Slack, Microsoft Teams) and project management tools (such as Trello, Asana), to achieve remote team collaboration and communication. These tools enable team members to share information, work together, and maintain effective communication remotely.
By expanding the SOHO network and enabling remote access, users can connect and access SOHO network resources from anywhere, improving work efficiency and flexibility. Cloud services and remote collaboration tools further enhance the ability to work and collaborate remotely, allowing team members to share information, work together, and stay connected.
Manage and maintain SOHO network
Managing and maintaining SOHO networks is the key to ensuring network security and stable performance. Here are some key practices and recommendations for managing and maintaining SOHO networks, along with explanations on configuring and updating network devices, monitoring network performance, and troubleshooting:
Key practices and recommendations:
- Documented network topology and configuration: Maintain an accurate network topology diagram and detailed network device configuration documents, including IP address, subnet mask, gateway, DNS settings, etc. These documents are very helpful for both troubleshooting and network expansion.
- Update network device software regularly: Keeping network device firmware and software updated is an important step in ensuring network security and performance. Regularly visit your device manufacturer’s website for the latest updates and security patches, and follow the guidelines for updates.
- Change passwords regularly: Change login passwords for network devices, routers, wireless access points, and other network devices regularly to ensure security. Use strong passwords and avoid reusing the same passwords on multiple devices.
- Restrict network access: Set appropriate access control lists (ACLs) and firewall rules as needed to restrict access to network resources. Allow only authorized users and devices to access the network, and block unnecessary inbound and outbound connections.
- Implement security policies: Develop and implement network security policies, including password policies, access control policies, security update policies, etc. Ensure that security policies are adhered to by all users and devices and are regularly reviewed and updated.
Configure and update network devices:
- Log in to the management interface: Use the management interface provided by the device manufacturer to log in to the configuration interface of the network device through the browser. This usually requires entering the device’s IP address and administrator credentials.
- Configure network parameters: Configure the device’s IP address, subnet mask, gateway and DNS settings according to network requirements. Make sure the device is on the correct subnet and communicating correctly with other devices.
- Configure security settings: Enable appropriate security settings, such as firewall rules, access control lists, remote access settings, etc., to enhance network security. Follow the device manufacturer’s recommendations and best practices.
- Update firmware and software: Visit your device manufacturer’s website to find the latest firmware and software updates. Download the update file and follow the device manufacturer’s guidelines for updating. Make sure to back up the device configuration before updating.
Monitor network performance and troubleshooting:
- Network monitoring tools: Use network monitoring tools, such as network performance monitors, traffic analysis tools, etc., to monitor network traffic, bandwidth utilization and device status in real time. This helps promptly identify and resolve network performance issues.
- Log analysis: Regularly check the logs of network devices to understand network activities, abnormal events and potential security threats. Log analysis can help identify problems and take appropriate actions for troubleshooting.
- Troubleshooting process: Establish a troubleshooting process to systematically diagnose and solve network problems. Track issues, step-by-step troubleshooting possible causes, and document solutions for future reference.
- Seek professional support: If you encounter complex network problems or unresolved failures, please consider seeking professional network support. Network experts can provide professional diagnosis and solutions to ensure the normal operation of the network.
By following these practices and recommendations for managing and maintaining your SOHO network, you can ensure network security and stable performance. Regularly updating network devices, configuring security settings, monitoring network performance, and establishing troubleshooting procedures are all important steps in ensuring the proper functioning of your network. Maintaining a healthy network environment will increase productivity and protect your data and resources from potential security threats.
Overview:
Thank you for reading our blog! Through the in-depth discussion of this article, you will have a more comprehensive understanding of the role and advantages of SOHO (Small Office/Home Office) networks in small offices and home offices. SOHO network is an ideal choice for smaller office environments. It has the characteristics of flexibility, scalability and efficiency. In a SOHO network, key devices such as routers, switches and wireless access points play an important role in helping to establish and manage network connections. At the same time, key technologies such as wireless LAN (WLAN) and virtual private network (VPN) make remote access and secure communication possible.
Managing and maintaining the SOHO network is the key to ensuring stable network operation. We provide some practices and suggestions for managing and maintaining SOHO networks, including configuring and updating network devices, monitoring network performance, and troubleshooting. By choosing our products, you will get reliable network equipment and professional support to help you build and maintain an efficient SOHO network.
SOHO Network FAQ
A typical SOHO network consists of several components, including computers or laptops, routers, switches, modems, printers, wireless access points, and network storage devices.
The purpose of a SOHO network is to enable communication, resource sharing, and internet connectivity for small office or home office users. It allows users to connect their devices, share files, access shared resources, and connect to the internet.
SOHO networks commonly use wired and wireless connections. Wired connections include Ethernet cables for connecting devices to routers or switches. Wireless connections are established using Wi-Fi technology, allowing devices to connect to the network without physical cables.
In most cases, a dedicated server is not necessary for a SOHO network. SOHO networks typically rely on file sharing and resource sharing among connected devices, eliminating the need for a separate server. However, network-attached storage (NAS) devices can be used for centralized file storage and access.
Securing a SOHO network involves implementing security measures such as setting strong and unique passwords, enabling network encryption (WPA2 or WPA3) for Wi-Fi, using a firewall, keeping devices and software up to date, and regularly backing up data.
Yes, one of the advantages of a SOHO network is that it allows multiple devices to be connected simultaneously. Computers, laptops, smartphones, tablets, printers, and other network-enabled devices can all be connected to the network.
File and resource sharing on a SOHO network can be achieved by setting up shared folders on individual devices or by using a network-attached storage (NAS) device. Users can then access these shared resources from other connected devices.
Yes, it is possible to access your SOHO network remotely. By setting up Virtual Private Network (VPN) connectivity, you can securely access your network resources from outside the office or home office environment.
Some common challenges in managing a SOHO network include ensuring reliable and stable network connectivity, addressing security concerns, managing device compatibility and updates, and troubleshooting network issues without dedicated IT support.