10Gb Ethernet undoubtedly plays an important role in the network. This article will explore the types of optical fibers suitable for 10Gb Ethernet. We will first define the basic physical structure and transmission mechanism of optical fibers, and briefly introduce the common types of optical fibers and their characteristics. Next, we will explain the specific requirements of 10Gb Ethernet for optical fiber transmission performance and analyze the key technical indicators that affect the selection of 10Gb optical fibers.
We will describe the transmission capacity of single-mode optical fiber in 10Gb Ethernet and explain its advantages in long-distance applications. In addition, we will explain the transmission characteristics of multimode optical fiber in 10Gb Ethernet and explore its advantages in short-distance applications. Finally, we will compare the differences between the two optical fibers in terms of bandwidth, loss, etc., and analyze the considerations for choosing single-mode or multimode optical fiber in 10Gb applications.
Overview of Optical Fiber Transmission Technology
Let me give you a brief introduction to the basics of optical fiber transmission technology.
Basic physical structure and transmission mechanism of optical fiber:
(1) Physical structure of optical fiber:
- Optical fiber consists of core, cladding, buffer layer and outer sheath.
- The core layer is a transparent material, such as glass or plastic, responsible for the transmission of optical signals.
- The refractive index of the cladding material is slightly lower than that of the core layer, which is used to limit the propagation of optical signals in the core.
(2) Transmission mechanism of optical signals:
- The optical signal undergoes multiple total reflections inside the core layer and is transmitted along the length of the optical fiber.
- The function of the cladding material is to prevent the optical signal from leaking outward and ensure that the optical signal propagates within the core layer.
- This total internal reflection transmission mechanism can achieve low-loss transmission of optical signals in optical fibers.
(3) Advantages of fiber transmission:
- Large bandwidth: It can support ultra-high-speed data transmission of up to hundreds of Gbps.
- Low loss: The loss of single-mode fiber is only 0.2dB/km, which is much better than copper wire.
- Anti-interference: Fiber is not affected by electromagnetic interference, and the transmission signal is more stable and reliable.
- Small size: The diameter of the fiber is only 0.1-0.25mm, which is easy to wire and manage.
Common fiber types and their characteristics:
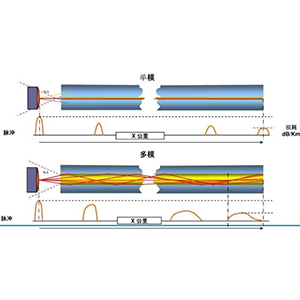
(1) Single-mode fiber (SMF):
- Only a single mode of light is allowed to propagate in the core layer.
- It has a long transmission distance and large bandwidth, and is generally used in trunk lines and backbone networks.
- Small core diameter (8-10μm), easy to connect and transmit, but expensive.
(2) Multi-mode Fiber (MMF):
- Allows multiple modes of light to propagate in the core layer.
- Large core diameter (50-100μm), relatively easy to connect, and low cost.
- Short transmission distance (2-3km), limited bandwidth, generally used in building/campus networks.
(3) Plastic Optical Fiber (POF):
- Optical fiber made of plastic material, cheap.
- Short transmission distance (less than 100m), limited bandwidth, mostly used for indoor wiring.
- Easy to install, suitable for DIY and non-professional operation.
In short, different types of optical fibers have their own applicable scenarios and performance characteristics, and users need to choose according to actual needs.
10Gb Ethernet optical fiber requirements
10Gb Ethernet does have strict requirements on optical fiber transmission performance. Let me introduce the relevant content to you in detail.
Specific requirements of 10Gb Ethernet on optical fiber transmission performance:
(1) Bandwidth requirements:
- 10Gb Ethernet requires at least 10Gbps optical fiber transmission bandwidth.
- Considering the transceiver equipment and other system overhead, a higher-speed optical fiber should be used.
(2) Transmission distance requirements:
- The maximum transmission distance specified by the 10Gb Ethernet standard is 40km (single-mode fiber) and 550m (multi-mode fiber).
- It is necessary to select a fiber type that can support the required transmission distance.
(3) Low loss requirements:
- 10Gb Ethernet has strict restrictions on fiber loss, requiring the loss to be less than 2.6dB.
- This requires the selection of low-loss fiber and ensuring the connection quality.
(4) Low dispersion requirements:
- 10Gb Ethernet also has certain requirements for dispersion, which needs to be less than 18ps/nm*km.
- Excessive dispersion will cause signal distortion and limit the transmission distance.
(5) Reliability requirements:
- As a high-speed backbone network, 10Gb Ethernet requires extremely high reliability and stability.
- The optical fiber must withstand the test of harsh environments to ensure long-term stable operation.
Key technical indicators affecting the selection of 10Gb optical fiber:
(1) Optical fiber type:
- Single-mode optical fiber is more suitable for long-distance 10Gb Ethernet transmission.
- Multi-mode optical fiber is suitable for short-distance transmission, such as internal wiring in buildings.
(2) Optical fiber core diameter:
- The common core diameter of single-mode optical fiber is 8-10μm, and that of multi-mode optical fiber is 50-100μm.
- A smaller core diameter is conducive to achieving low loss and low dispersion.
(3) Fiber attenuation coefficient:
- Fibers with lower attenuation coefficients are more suitable for 10Gb Ethernet transmission.
- Typical requirements are less than 0.5dB/km (single-mode) or 3.5dB/km (multi-mode).
(4) Dispersion characteristics:
- The dispersion coefficient must be less than 18ps/nm*km to ensure signal integrity.
- Special dispersion-compensating fiber helps suppress dispersion.
(5) Anti-interference performance:
- The fiber must have excellent electromagnetic anti-interference capabilities to ensure stable transmission.
- It is critical to adopt reasonable fiber wiring and connection methods.
In short, the bandwidth, transmission distance, loss, dispersion and other indicators of optical fiber will affect the actual performance of 10Gb Ethernet. Therefore, these key technical parameters need to be fully considered when selecting optical fiber.
Application of single-mode optical fiber in 10Gb applications
Let me introduce you in detail the performance and advantages of single-mode optical fiber in 10Gb Ethernet applications.
Transmission capacity of single-mode optical fiber in 10Gb Ethernet:
(1) Bandwidth capacity:
- Single-mode optical fiber can provide a transmission bandwidth of more than 10Gbps, which fully meets the requirements of 10GbE.
- In fact, the actual bandwidth of single-mode optical fiber can reach tens or even hundreds of Gbps.
(2) Transmission distance:
- The 10GbE standard stipulates that the maximum transmission distance of single-mode optical fiber can reach 40km.
- In actual applications, the transmission distance of single-mode optical fiber under good conditions can reach 80-100km.
(3) Low loss:
- The loss coefficient of single-mode optical fiber is usually less than 0.5dB/km.
- Even at a transmission distance of 40km, the total loss can be controlled within 2.6dB.
(4) Low dispersion:
- The dispersion characteristics of single-mode optical fiber are very good and can be controlled within 18ps/nm*km.
- This allows 10Gb signals to be transmitted over long distances without suffering from severe dispersion distortion.
Advantages of single-mode fiber in long-distance applications:
(1) Transmission distance advantage:
- Single-mode fiber can support longer transmission distances, up to 100km.
- This greatly reduces the number of relay stations and simplifies network deployment.
(2) Bandwidth advantage:
- Single-mode fiber has a wider bandwidth and can easily meet the bandwidth requirements of 10Gb Ethernet.
- It also has the potential to be further expanded to 40/100GbE.
(3) Low loss advantage:
- The low loss characteristics of single-mode fiber make the signal quality better in long-distance transmission.
- No need for too many repeater amplifiers, reducing system cost and complexity.
(4) Anti-interference advantage:
- Due to the small core size, single-mode fiber is less susceptible to electromagnetic interference.
- Improves the stability and reliability of the transmission signal.
(5) Compatibility advantage:
- Single-mode fiber technology is relatively mature and has good compatibility with mainstream 10Gb Ethernet equipment.
- Easy to integrate seamlessly with existing network infrastructure.
In short, single-mode fiber has a unique advantage in the backbone network application of 10Gb Ethernet due to its excellent long-distance transmission performance.
Application of multimode fiber in 10Gb applications
Let me analyze the characteristics and advantages of multimode fiber in 10Gb Ethernet applications.
Transmission characteristics of multimode fiber in 10Gb Ethernet:
(1) Bandwidth capability:
- The bandwidth of multimode fiber is slightly limited compared to single-mode fiber, generally up to 10Gbps.
- This barely meets the bandwidth requirements of 10Gb Ethernet, but cannot provide too much redundancy.
(2) Transmission distance:
- The 10GbE standard stipulates that the maximum transmission distance of multimode optical fiber is 550 meters.
- In actual applications, multimode optical fiber can usually reach a transmission distance of 1-2 kilometers.
(3) Loss characteristics:
- The loss coefficient of multimode optical fiber is generally around 3.5dB/km.
- In short-distance transmission of about 550 meters, the total loss can be controlled within 2.6dB.
(4) Dispersion characteristics:
- The dispersion performance of multimode optical fiber is poor, and the dispersion coefficient is usually around 18ps/nm*km.
- This will limit the transmission distance on 10Gb Ethernet.
Advantages of multimode fiber in short-distance applications:
(1) Cost advantage:
- The cost of multimode fiber is significantly lower than that of single-mode fiber, which is more obvious in short-distance applications.
- Suitable for budget-limited or cost-sensitive application scenarios.
(2) Installation convenience:
- The core diameter of multimode fiber is larger (50-100μm), and splicing and wiring are relatively simple.
- Even non-professionals can perform DIY wiring and installation.
(3) Compatibility advantage:
- Multimode fiber is more compatible with the interfaces of existing LAN switches and routers.
- Can seamlessly connect with a large number of deployed 10GbE devices.
(4) Engineering implementation advantages:
- Multimode fiber has lower installation and maintenance costs and is easier to deploy and manage.
- Particularly suitable for 10Gb Ethernet applications within a limited range such as buildings and campuses.
(5) Advantages of no repeater:
- For short-distance transmission within 550 meters, multimode fiber can be achieved without repeater amplification.
- Simplifies network topology and reduces system complexity.
In short, for specific short-distance high-speed network applications, multimode fiber still has some unique advantages. This makes it another choice for 10Gb Ethernet deployment.
Performance comparison between single-mode fiber and multimode fiber
Let me compare the differences between single-mode fiber and multimode fiber in key performance indicators in detail, and analyze the key considerations for choosing which fiber to use in 10Gb Ethernet applications.
Performance comparison between single-mode fiber and multimode fiber:
(1) Bandwidth performance:
- The bandwidth of single-mode fiber can reach tens or even hundreds of Gbps, far
- The bandwidth of multimode fiber is usually around 10Gbps, which just meets the 10GbE standard.
(2) Transmission distance:
- Single-mode fiber can support long-distance transmission of 40km (standard) or even 100km.
- The transmission distance of multimode fiber is only 550 meters (standard) or 1-2 kilometers (actual).
(3) Optical signal loss:
- The loss coefficient of single-mode fiber is less than 0.5dB/km, and the loss is lower.
- The loss coefficient of multimode fiber is generally around 3.5dB/km, and the loss is higher.
(4) Dispersion characteristics:
- The dispersion coefficient of single-mode fiber can be controlled within 18ps/nm*km, and the dispersion is low.
- The dispersion coefficient of multimode fiber is usually higher than 18ps/nm*km, and the dispersion is large.
(5) Cost and installation:
- The cost of single-mode fiber is higher, and the installation and maintenance are also more complicated.
- The cost of multimode fiber is lower, and the installation and maintenance are easier.
In general, single-mode fiber is superior to multimode fiber in terms of bandwidth, transmission distance and signal quality, but the cost and installation complexity are higher.
Considerations for choosing single-mode or multimode fiber in 10Gb applications:
(1) Transmission distance requirements:
- If long-distance (>2km) 10Gb Ethernet transmission is required, single-mode fiber is a better choice.
- For short-distance (<550m) applications, multimode fiber may have a cost advantage.
(2) Bandwidth redundancy requirements:
- If a larger bandwidth redundancy space is required to cope with future demand growth, single-mode fiber is more suitable.
- For scenarios where only 10Gb Ethernet is required, multimode fiber can also do the job.
(3) Network complexity requirements:
- If simplicity of network deployment and maintenance is sought, multimode fiber will be more suitable.
- For critical networks that require higher reliability and manageability, single-mode fiber has more advantages.
(4) Budget cost considerations:
- If the budget is limited, multimode fiber will be more attractive due to its lower hardware and installation costs.
- For applications that can afford higher fiber costs, single-mode fiber is a better choice.
In short, in 10Gb Ethernet applications, choosing single-mode or multimode fiber requires weighing multiple factors such as transmission distance, bandwidth requirements, complexity and cost to find the solution that best suits your needs.
Summary
Rational selection of fiber types suitable for 10Gb Ethernet is crucial to building a high-performance network. Our company has long focused on the research and development and production of optical communication equipment and its supporting products, and has rich industry experience. Our single-mode fiber and multi-mode fiber products are at the industry-leading level in terms of optical performance and reliability, and can meet your demanding needs for 10Gb Ethernet construction.
Whether you need to deploy in a data center, a telecommunications office, or an enterprise campus environment, we can provide you with customized fiber solutions. At the same time, our professional team will provide you with a full range of technical support, including on-site surveys, product recommendations, and installation and commissioning guidance. Contact us now to learn more about the types of fiber suitable for 10Gb Ethernet.
10GB Fiber FAQ
10GbE networks commonly use either multi-mode fiber (MMF) or single-mode fiber (SMF), depending on the distance requirements and network design.
MMF is a type of optical fiber with a larger core diameter, allowing multiple modes of light to propagate. It is typically used for shorter distances in 10GbE networks.
SMF is an optical fiber with a much smaller core diameter, designed to carry only a single mode of light. It is used for longer distances in 10GbE networks.
For short distances (up to a few hundred meters), multi-mode fiber (MMF) with OM3 or OM4 specifications is commonly used in 10GbE networks.
For longer distances (up to tens of kilometers), single-mode fiber (SMF) is typically used in 10GbE networks, providing greater reach and signal integrity.
OM3 and OM4 are types of multi-mode fiber with enhanced bandwidth capabilities. OM3 supports 10GbE up to 300 meters, while OM4 supports 10GbE up to 400 meters.
Yes, common connectors include LC (for both MMF and SMF), SC (mostly for MMF), and sometimes MPO/MTP connectors (for MMF in high-density applications).
Yes, 10GbE can operate over existing fiber installations, provided the fiber meets the specifications required for the desired distance and data rate.
SMF offers greater bandwidth and longer reach compared to MMF, making it suitable for extended distances and future scalability in 10GbE networks.
Consider factors such as distance requirements, existing infrastructure, budget, and future growth plans when selecting between MMF and SMF for 10GbE deployments.